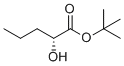
Tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate is a chemical compound that has attracted attention in the field of organic chemistry and pharmacology due to its potential applications in the synthesis of bioactive molecules. The compound belongs to a class of esters and is characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group at the 2-position of a pentanoate chain, attached to a tert-butyl group. The chiral center at the 2-position gives the molecule enantiomeric properties, with the (R)-configuration being of particular interest in medicinal chemistry due to its enhanced biological activity in some cases.
The discovery of tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate can be traced to efforts in asymmetric synthesis, where researchers sought methods to produce chiral compounds with high enantiomeric purity. The (R)-enantiomer of the compound is particularly useful in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates and in the design of compounds with specific stereochemistry that enhances their efficacy or reduces side effects. The presence of the hydroxyl group in combination with the tert-butyl ester group contributes to the compound’s stability and solubility, which are key factors in its potential applications.
The synthesis of tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate typically involves stereoselective reactions, where catalysts are used to direct the formation of the desired enantiomer. This may include the use of chiral reagents or enzymes that promote the selective addition of functional groups at the correct positions on the pentanoate chain. The use of tert-butyl esters in synthesis is common due to their ability to enhance the solubility and ease of purification of the compound, as well as their stability under various reaction conditions.
In terms of application, tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate is primarily used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other bioactive compounds, particularly those used in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. The compound’s ability to serve as a chiral building block makes it valuable in the synthesis of more complex molecules with specific biological activities. For example, it may be used in the synthesis of anti-inflammatory agents, analgesics, or other therapeutic compounds that require a precise configuration for optimal activity. Additionally, due to its chemical structure, tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate can be incorporated into molecules designed for the treatment of various diseases or as a precursor for the development of novel synthetic routes in drug discovery.
In the broader context, the compound serves as an example of how chiral synthesis can be leveraged to produce molecules with enhanced activity and selectivity. As interest in asymmetric catalysis and green chemistry grows, compounds like tert-butyl (R)-2-hydroxypentanoate continue to play a crucial role in the development of sustainable and effective synthetic methodologies.
|




 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details