Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shenzhen Nexconn Pharmatechs Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19068605196 | |||
 |
jason.deng@nexconn.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Thiophene compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate |
| Molecular Structure | 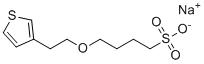 |
| Molecular Formula | C10H15NaO4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 286.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 701917-11-5 |
| SMILES | C1=CSC=C1CCOCCCCS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P270-P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313-P301+P312+P330 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate is a chemical compound that belongs to the category of organosulfonates, which are important in various chemical and industrial applications. The compound contains a sulfonate group (-SO3Na) attached to a butane backbone, with an ethoxy group linked to a thiophene ring. This structure imparts both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties, making it useful in several fields, particularly in organic synthesis and materials science. The discovery of sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate is linked to the ongoing research into functionalized sulfonates and their roles in enhancing the properties of organic materials. Thiophene derivatives are widely known for their unique electronic and optical properties, which make them valuable in the development of organic electronics, such as organic semiconductors and organic photovoltaic cells. By modifying the thiophene structure with an ethoxy group and linking it to a sulfonate group, researchers have designed molecules with improved solubility, stability, and charge-transport characteristics. This compound has found particular interest in the development of surfactants and emulsifiers due to its amphiphilic nature. The sulfonate group offers water solubility, while the thiophene and ethoxy groups contribute to the compound’s ability to interact with organic phases. As a result, sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate can be used in the formulation of cleaning agents, detergents, and other surfactant-based products where both water and oil phases need to be stabilized. In addition to its applications as a surfactant, sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate has potential uses in the preparation of novel organic materials for electronic devices. The unique combination of thiophene, ethoxy, and sulfonate groups allows for the modulation of the compound’s electronic properties, which can be harnessed in the design of advanced organic semiconductors. These materials are of particular interest for use in flexible electronics, thin-film transistors, and other emerging technologies in organic electronics. Another promising application of sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate lies in its use as a building block for the synthesis of more complex molecules. The compound can serve as a functionalized monomer in polymerization reactions, leading to the formation of conductive polymers with tailored properties. These polymers can be utilized in sensors, display devices, and energy storage systems, where specific electronic and mechanical properties are required. While the exact scope of its applications continues to be explored, sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate holds significant promise in a variety of technological fields. Its versatile chemical structure enables its use in multiple industries, from materials science and electronics to cleaning and emulsification. As research continues, its potential as a key component in the development of next-generation organic materials and devices is likely to expand. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Sodium 4-(2-(thiophen-3-yl)ethoxy)butane-1-sulfonate |