Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Cheng Du Chenlv Herb Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18981728582 | |||
 |
chenlvherb@126.com | |||
 |
WeChat: Cheng Du Chenlv Herb Co., Ltd. | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Natural product >> Flavonoids |
|---|---|
| Name | Fisetin Hydrate |
| Synonyms | 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one--water (1/1) |
| Molecular Structure | 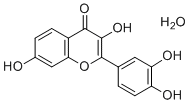 |
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 304.25 |
| CAS Registry Number | 345909-34-4 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2=C(C(=O)C3=C(O2)C=C(C=C3)O)O)O)O.O |
| Solubility | water: 0.222 mg/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Fisetin hydrate is the hydrated form of fisetin, a naturally occurring flavonol belonging to the flavonoid class of polyphenolic compounds. Flavonoids are widely distributed in the plant kingdom and are known for their roles in pigmentation, growth regulation, and protection against environmental stressors. Fisetin was first isolated in the late 19th century from smoke bush (*Rhus cotinus*), where it occurs as a natural yellow pigment. The compound is also found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, including strawberries, apples, persimmons, onions, and cucumbers. The hydrated form refers to the presence of water molecules associated with the crystalline structure of fisetin, which may affect its solubility and stability but does not alter its fundamental molecular framework. The discovery of fisetin and related flavonoids marked an important stage in phytochemistry, as scientists in the 19th and early 20th centuries sought to characterize natural pigments and their properties. Early methods involved solvent extraction and crystallization, followed by spectroscopic techniques and chemical derivatization to identify functional groups. With advances in analytical chemistry, the structure of fisetin was confirmed as 3,3',4',7-tetrahydroxyflavone, characterized by multiple hydroxyl substituents that contribute to its antioxidant properties. The hydrate form was recognized during crystallization and purification processes, a common occurrence for polyphenolic compounds due to their affinity for hydrogen bonding with water. Applications of fisetin hydrate are largely tied to the broader biological activities of fisetin. One of its most notable properties is its antioxidant activity, which arises from the ability of the hydroxyl groups to donate electrons and neutralize free radicals. This makes fisetin an important subject of research in the field of oxidative stress and its role in aging and disease. Beyond antioxidant activity, fisetin has been studied for its potential to modulate signaling pathways related to inflammation, apoptosis, and cell cycle regulation. The hydrate form, by influencing solubility and bioavailability, has been examined for potential improvements in pharmacological application compared to the anhydrous compound. In biomedical research, fisetin hydrate has been investigated for its neuroprotective properties, including effects on memory and learning in preclinical models. Studies have suggested that it may influence pathways involved in synaptic plasticity and protect neurons against oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. Its potential anti-inflammatory activity has also been explored, with evidence showing modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibition of key signaling enzymes. In oncology research, fisetin and its hydrate form have been tested for their potential to induce apoptosis in cancer cell lines and inhibit tumor growth in experimental models. These applications underscore the compound’s importance in ongoing studies of natural product-based therapeutics. Outside of medicine, fisetin hydrate has applications in food science and nutraceuticals. As a naturally occurring pigment with antioxidant properties, it is of interest for use in dietary supplements and functional foods. Its stability in the hydrated form can provide advantages in formulation, especially in aqueous systems where solubility is a concern. The compound has also been considered in cosmetic formulations, where its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may contribute to skin health and protection against environmental stressors. While fisetin hydrate is not yet approved as a therapeutic drug, it exemplifies the broader interest in plant-derived flavonoids as potential bioactive agents. Its discovery and subsequent research highlight the importance of natural products chemistry in identifying compounds with diverse applications across health, nutrition, and materials science. Continued investigation into its pharmacokinetics, stability, and clinical relevance is necessary to fully realize its potential. References Grynkiewicz G, Demchuk OM (2019) New Perspectives for Fisetin. Frontiers in Chemistry 7:697 DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00697 Szymczak J, Cielecka-Piontek J (2023) Fisetin—In Search of Better Bioavailability—From Macro to Nano Modifications: A Review. *International Journal of Molecular Sciences* 24(18) 14158 DOI: 10.3390/ijms241814158 Krishnakumar IM, Jaja-Chimedza A, Joseph A, Balakrishnan A, Maliakel B, Swick A (2022) Enhanced bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of a novel hybrid-hydrogel formulation of fisetin orally administered in healthy individuals: a randomised double-blinded comparative crossover study. Journal of Nutritional Science 11:e74 DOI: 10.1017/JNS.2022.72 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Fisetin Hydrate |