Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Inorganic chemical industry >> Inorganic salt >> Metal nitrates and nitrites |
|---|---|
| Name | Palladium nitrate |
| Synonyms | Palladous nitrate; Palladium (II) nitrate |
| Molecular Structure | 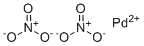 |
| Molecular Formula | Pd.(NO3)2 |
| Molecular Weight | 230.43 |
| CAS Registry Number | 10102-05-3 |
| EC Number | 233-265-8 |
| SMILES | [N+](=O)([O-])[O-].[N+](=O)([O-])[O-].[Pd+2] |
| Melting point | 870 ºC (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Solubility | soluble water (20 ºC (Expl.) |
| Hazard Symbols |





 GHS03;GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 DangerGHS03;GHS05; Details
GHS03;GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 DangerGHS03;GHS05; Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H271-H272-H290-H302-H314-H318-H400-H410 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P220-P234-P260-P264-P264+P265-P270-P273-P280-P283-P301+P317-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P306+P360-P316-P317-P321-P330-P363-P370+P378-P371+P380+P375-P390-P391-P405-P406-P420-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Palladium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pd(NO3)2, consisting of palladium in the +2 oxidation state coordinated by nitrate anions. It is typically encountered as a hydrate, often in the form of a yellow-brown crystalline solid that is soluble in water and various polar organic solvents. Palladium nitrate is widely used as a precursor in palladium chemistry and serves an important role in catalyst preparation, materials synthesis, and analytical applications. The compound can be prepared by dissolving palladium metal, palladium(II) oxide, or palladium(II) chloride in nitric acid under controlled conditions. This reaction yields a solution of Pd(NO3)2, which may be concentrated to obtain the solid hydrate. Care must be taken during the preparation, as concentrated nitric acid and nitrogen oxides are corrosive and toxic. In its solid state, palladium nitrate exists primarily in hydrated form. The exact composition of the hydrate can vary depending on the drying and crystallization conditions. The nitrate ligands coordinate to the palladium center either through bidentate or monodentate bonding modes, and the coordination geometry around palladium is typically square planar, consistent with the d8 electron configuration of Pd(II). In aqueous solution, palladium nitrate can form various complex ions depending on pH and concentration, including solvated Pd2+ ions and nitrate-coordinated species. Palladium nitrate is most widely used as a palladium source in the preparation of supported palladium catalysts. These catalysts are employed in numerous reactions, including hydrogenation, oxidation, carbon-carbon coupling reactions (such as Suzuki–Miyaura and Heck reactions), and environmental catalytic processes. The compound is often impregnated onto supports such as activated carbon, alumina, silica, or zeolites and then thermally decomposed or reduced to generate metallic palladium nanoparticles or oxide species. In materials chemistry, Pd(NO3)2 is used to introduce palladium into ceramic matrices, conductive inks, and thin films. Thermal decomposition of palladium nitrate produces palladium oxide or metallic palladium, depending on the atmosphere, making it suitable for deposition processes in microelectronics and sensor fabrication. In some synthetic procedures, it is also used as an oxidant or as a source of palladium for the generation of coordination complexes. In analytical chemistry, palladium nitrate is used as a reagent in gravimetric and spectroscopic methods, particularly for detecting specific anions or organic functional groups through complexation or redox reactions. The compound has been employed in standard methods for the determination of sulfur compounds due to palladium’s affinity for sulfide and thiol groups. Due to the presence of nitrate anions, palladium nitrate can act as an oxidizing agent and should be handled with appropriate precautions. It is corrosive and may release nitrogen oxides upon decomposition. Handling requires gloves, eye protection, and ventilation. It should be stored in tightly sealed containers away from reducing agents, flammable materials, and strong bases. The decomposition of palladium nitrate upon heating typically occurs in multiple steps. Initially, water is lost from the hydrate, followed by decomposition of nitrate ligands, which results in the release of nitrogen oxides and formation of palladium oxide (PdO) or metallic palladium at elevated temperatures. This thermal behavior is exploited in catalyst activation procedures and materials synthesis. In summary, palladium nitrate is a versatile Pd(II) salt used extensively as a precursor for catalysts, coordination compounds, and advanced materials. Its solubility and reactivity make it valuable for various applications in synthetic, analytical, and industrial chemistry. Proper handling and storage are essential due to its oxidizing nature and toxicity. References 2024. Pd supported Al-BDC MOF for efficient and selective N-methylation of amines under solventless conditions. Emergent Materials, 7(3). DOI: 10.1007/s42247-024-00669-2 2024. Hydrophobic Modification of Small-Pore Pd-SSZ-13 Zeolites for Catalytic Methane Combustion. Topics in Catalysis, 67(15-16). DOI: 10.1007/s11244-024-01923-x 2024. Al2O3-Flower Anchoring Pd Catalyst for Acetylene Selective Hydrogenation: A Compartmentalizing Strategy Promotes Metal Dispersion and Maintains Stability. Catalysis Letters, 154(10). DOI: 10.1007/s10562-024-04693-z |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Palladium nitrate |