Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Name | Bis(3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfane |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | 1-(3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfanyl-3,5-difluorobenzene |
| Molecular Structure | 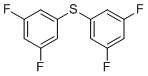 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H6F4S |
| Molecular Weight | 258.23 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1801970-32-0 |
| SMILES | C1=C(C=C(C=C1F)SC2=CC(=CC(=C2)F)F)F |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H318 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P270-P280-P301+P312-P305+P351+P338-P310-P330-P501 Details |
| Transport Information | UN 3077 |
| SDS | Available |
|
Bis(3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfane, also known as DFPS, is a synthetic compound characterized by a sulfur atom bonded to two 3,5-difluorophenyl groups. The discovery of bis(3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfane stems from the search for compounds with enhanced electronic properties. In the mid-20th century, researchers began to study the effects of fluorination on aromatic compounds with the goal of improving their stability, reactivity, and electronic properties. DFPS is part of this search and is characterized by a sulfur atom attached to two benzene rings, with the 3- and 5-positions of the benzene rings substituted with fluorine atoms. The presence of the fluorine atom introduces an electron-withdrawing effect that alters the electronic environment of the benzene rings and enhances the overall reactivity of the compound. The synthesis of DFPS generally involves the reaction of 3,5-difluorophenylthiol with a suitable electrophile to form the sulfane. This process highlights the ease of formation of the compound and the effect of fluorine on the chemical reactivity of the phenyl groups. DFPS is presented as a crystalline solid with remarkable chemical stability and unique electronic properties that can be used in a variety of applications. DFPS is used in the development of organic semiconductors. Its aromatic structure, combined with electron-withdrawing fluorine atoms, enhances charge transport properties for applications in organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and organic photovoltaics (OPVs). These semiconductors are essential components in flexible electronics and advanced display technologies. In photovoltaic cells, DFPS helps create materials that can efficiently absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. Fluorine atoms increase the electron affinity of the compound, improving the efficiency of charge separation and transport within the photovoltaic material. This makes DFPS an important ingredient in the development of next-generation solar cells. DFPS can also be used to develop dielectric materials, which are essential for insulation and storage of electrical energy in electronic devices. Its unique electronic properties allow for the fabrication of materials with high dielectric constants and thermal stability, which improves the performance and reliability of electronic components. In medicinal chemistry, DFPS can serve as a scaffold for the development of new drugs. Its structure allows for the introduction of various functional groups, resulting in derivatives with potential therapeutic properties. Researchers have used DFPS to design compounds that target different biological pathways, aiming to improve the efficacy and selectivity of drugs. DFPS derivatives have been intensively studied for their potential as anticancer agents. The presence of fluorine atoms can enhance the ability of the compound to interact with biological targets and improve its stability in biological environments. Research focuses on optimizing these derivatives to effectively inhibit cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis. The compound is also used to develop enzyme inhibitors. DFPS derivatives can interact with enzyme active sites, inhibiting their function. This application is particularly important in designing enzyme inhibitors involved in disease pathways, providing potential treatments for diseases such as cancer and infectious diseases. DFPS is used in cross-coupling reactions such as Suzuki-Miyaura and Stille couplings. These reactions enable the formation of carbon-carbon bonds, which are essential for building complex organic molecules. The fluorine atoms on the benzene ring affect the reactivity of the compound, allowing the creation of a variety of molecular structures. As a precursor, DFPS can be further functionalized to introduce other substituents. This versatility allows the synthesis of a wide range of fluorinated aromatic compounds with customized electronic and steric properties for specific applications in materials science and pharmaceuticals. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bis(3,5-difluorophenyl)sulfane |