Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Xi'an Yuri Solar Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (029) 8110-1199 | |||
 |
jiaop@yurisolar.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: plt18092602675 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Piperazine |
|---|---|
| Name | Piperazine hydroiodide |
| Molecular Structure | 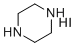 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11IN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 214.05 |
| CAS Registry Number | 56310-12-4 |
| EC Number | 164-341-8 |
| SMILES | C1CNCCN1.I |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P264+P265-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364 Details |
|
Piperazine hydroiodide (C4H10N2·2HI) is a crystalline salt formed by the reaction of piperazine, a six-membered heterocyclic diamine, with hydroiodic acid. The free base piperazine, first synthesized in the late 19th century, is an important compound in both pharmaceutical and chemical research due to its symmetrical diamine structure and its presence as a key scaffold in many bioactive molecules. Converting piperazine into its hydroiodide salt provides a stable, non-volatile, and readily handled crystalline solid that is useful for laboratory and preparative purposes. The discovery of piperazine itself dates back to its preparation from piperazine derivatives of piperidine, and since then it has been studied extensively as a versatile chemical intermediate. The hydroiodide salt form is not as widely encountered as other salts such as the dihydrochloride, but it has been prepared to provide researchers with a solid-state derivative that is less hygroscopic and more suitable for precise weighing, recrystallization, and storage. Structurally, piperazine hydroiodide consists of protonated piperazine cations, where both nitrogen atoms of the heterocyclic ring can accept protons, paired with iodide anions. This leads to a stable ionic lattice maintained by hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. Crystallographic studies of piperazine salts, including the hydroiodide, have contributed to understanding the molecular packing and solid-state behavior of simple amine salts, which is of particular relevance to pharmaceutical formulation science. The compound finds use primarily in laboratory research. It has been utilized as a source of piperazine in synthetic organic chemistry, where the salt is converted back to the free base under basic conditions. This provides a convenient way to store and handle the compound without the volatility or instability sometimes associated with the free base. Its solubility in water and polar solvents further facilitates its use in chemical reactions. In pharmacology, piperazine itself has a long history of use as an anthelmintic agent, particularly in the form of salts such as piperazine citrate or piperazine phosphate, which have been used in the treatment of intestinal roundworm infections. While the hydroiodide form is not employed in therapy, it serves as a useful model compound for studying the physicochemical properties of piperazine salts and their interactions with various counterions. Research into the physicochemical properties of piperazine hydroiodide has also contributed to the broader field of salt formation in medicinal chemistry. Salt selection is a critical process in drug development, as the counterion can strongly influence solubility, stability, bioavailability, and crystallinity. Piperazine hydroiodide provides a useful comparative system for exploring how different halide anions (chloride, bromide, iodide) affect the properties of otherwise similar organic salts. Applications of piperazine hydroiodide remain mainly experimental and academic. It is valuable for crystallographic analysis, comparative studies of amine salt forms, and as a precursor in synthesis. It also exemplifies the role of hydrohalide salts in stabilizing organic amines, highlighting how relatively simple modifications, such as conversion to a salt, can improve the practicality and usefulness of a compound in research settings. In summary, piperazine hydroiodide is a stable crystalline derivative of piperazine, obtained through its reaction with hydroiodic acid. While it has no widespread therapeutic or industrial application, it has significance in chemical research, particularly in the areas of crystallography, salt chemistry, and as a laboratory-stable precursor of piperazine for synthetic uses. Its role is primarily enabling, making the study and application of piperazine more practical in controlled laboratory contexts. References 1993. 26-1 - 26-96: CCl3I - C8H16B10I.BF4. Landolt-B�rnstein - Group III Condensed Matter. DOI: 10.1007/10057766_21 2019. Synthesis and characterization of piperazine-based organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. DOI: 10.1039/C9TC01234A 2023. Structural and optical properties of piperazine-based hybrid perovskites for optoelectronic applications. Chemical Physics Letters. DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2023.140345 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Piperazine hydroiodide |