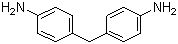
4,4'-Methylenedianiline, commonly referred to as MDA, is an organic compound with significant industrial importance. This aromatic amine is characterized by two aniline groups linked by a methylene bridge at the para position. The chemical structure of MDA, with its two amino groups, makes it highly reactive and a valuable intermediate in various chemical processes.
The discovery of 4,4'-methylenedianiline dates back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized as part of the broader exploration of amine compounds. MDA quickly gained attention for its utility in the production of polymers, particularly in the manufacture of polyurethane and epoxy resins. The compound is synthesized through a condensation reaction between formaldehyde and aniline, a process that yields a mixture of isomers, with 4,4'-MDA being the most prominent.
One of the primary applications of 4,4'-methylenedianiline is in the production of polyurethane, a versatile material used in various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. MDA serves as a precursor to methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), a crucial component in the synthesis of polyurethane. The reactivity of MDA allows for the formation of strong, durable polymers, making it an essential material in the production of foams, elastomers, and coatings. Polyurethane foams, for example, are widely used for insulation, cushioning, and packaging due to their lightweight and resilient properties.
In addition to its role in polyurethane production, 4,4'-methylenedianiline is also used in the manufacture of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, which are formed by the reaction of MDA with epichlorohydrin, are known for their excellent adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. These resins are widely used in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. The robustness of epoxy resins makes them suitable for applications in electronics, aerospace, and construction, where they are used to protect surfaces, bond materials, and provide structural integrity.
Despite its widespread industrial use, 4,4'-methylenedianiline is also recognized for its potential health and environmental hazards. MDA is classified as a probable human carcinogen, and exposure to it can lead to various health issues, including skin irritation, respiratory problems, and liver damage. As a result, strict regulations are in place to control its use and handling. Industries that utilize MDA are required to implement safety measures to protect workers and minimize environmental contamination.
The dual nature of 4,4'-methylenedianiline—its industrial importance and associated risks—has led to ongoing research into safer alternatives and methods to mitigate its hazards. Efforts are being made to develop MDA derivatives with reduced toxicity while maintaining its valuable chemical properties. Additionally, advancements in industrial processes aim to minimize exposure and improve the safety of handling and using MDA in various applications.
4,4'-Methylenedianiline remains a critical chemical in the production of polyurethane and epoxy resins, contributing to the creation of materials that are integral to modern industry and consumer products. However, its use is carefully regulated to balance its industrial benefits with the need to protect human health and the environment.
|





















 GHS06;GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Danger Details