Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Beijing Ribio Biotech. Inc. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 6266-4360 +86 13910960639 | |||
 |
sales@ribio.com.cn ribio@163.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Wuhu Huaren Science and Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (553) 584-2013 | |||
 |
wuhuhuaren@163.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Win-Win Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (577) 6449-8589 +86 15325081899 | |||
 |
sales@win-winchemical.com winwinchemical@gmail.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Amadis Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8992-5085 | |||
 |
sales@amadischem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Xinxiang Aurora Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (373) 308-8722 +86 18637352520 | |||
 |
info@aurora-biotech.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Nucleoside drugs >> Deoxynucleotides and their analogues |
|---|---|
| Name | 2'-Deoxyadenosine monohydrate |
| Synonyms | (2R,3S,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol;hydrate |
| Molecular Structure | 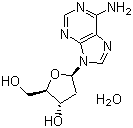 |
| Protein Sequence | A |
| Molecular Formula | C10H13N5O3.H2O |
| Molecular Weight | 269.26 |
| CAS Registry Number | 16373-93-6 |
| EC Number | 683-408-7 |
| SMILES | C1[C@@H]([C@H](O[C@H]1N2C=NC3=C(N=CN=C32)N)CO)O.O |
| Melting point | 186-189 ºC (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Water solubility | 0.3 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302 Details | ||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P301+P312 Details | ||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||
|
2'-Deoxyadenosine monohydrate is a nucleoside consisting of the purine base adenine linked to a deoxyribose sugar. The chemical formula for this substance is C10H13N5O3·H2O, and it plays a crucial role in the biochemical processes of living organisms, primarily in the synthesis of nucleic acids such as DNA. 2'-Deoxyadenosine is an important building block in DNA, as it is incorporated into the growing DNA chain during DNA replication. The hydroxyl group at the 3'-position of the sugar in deoxyribose differentiates it from ribose, which has a hydroxyl group at both the 2'- and 3'-positions, making it a component of RNA instead of DNA. The monohydrate form indicates that the compound includes one molecule of water per molecule of 2'-deoxyadenosine, a feature that can influence its crystallization and solubility properties. This compound is widely used in molecular biology and biochemistry. In particular, 2'-deoxyadenosine is involved in the synthesis of deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), which is one of the four nucleotide triphosphates required for DNA replication. The dATP molecule provides the adenine base during DNA synthesis, where it pairs with thymine through hydrogen bonds to form the base pair. Beyond its role in DNA synthesis, 2'-deoxyadenosine and its derivatives have been studied for their potential therapeutic applications. In the context of nucleoside analogs, certain modified forms of 2'-deoxyadenosine have shown promise as antiviral agents, particularly in the treatment of viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These modified nucleosides can interfere with viral replication by incorporating into viral DNA and terminating the elongation of the DNA strand. Additionally, the compound has relevance in research focused on the synthesis of oligonucleotides, where it is incorporated into synthetic DNA strands. This application is crucial in the fields of gene therapy, DNA sequencing, and the development of diagnostic tools. In conclusion, 2'-deoxyadenosine monohydrate is an essential component in the synthesis and structure of DNA. It serves as a building block for deoxyribonucleic acid, contributing to the stability and replication of genetic material. The compound’s applications in molecular biology, pharmaceutical development, and the synthesis of DNA make it a key substance in both scientific research and medicine. References 1989. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Landolt-B�rnstein - Group VII Biophysics. DOI: 10.1007/10384901_47 2009. Pd(0)/Cu(I)-Mediated Direct Arylation of 2'-Deoxyadenosines: Mechanistic Role of Cu(I) and Reactivity Comparisons with Related Purine Nucleosides. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 74(16). DOI: 10.1021/jo9012282 2015. Synthesis of boronic-acid-functionalized magnetic attapulgite for selective enrichment of nucleosides. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 407(12). DOI: 10.1007/s00216-015-8550-4 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2'-Deoxyadenosine monohydrate |