Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Zhengzhou Alfachem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0371) 5505-2911 | |||
 |
alfa5@alfachem.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate |
|---|---|
| Name | 5,8-Dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline |
| Molecular Structure | 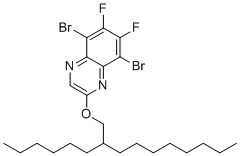 |
| Molecular Formula | C24H34Br2F2N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 564.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2269476-12-0 |
| EC Number | 891-320-7 |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC(CCCCCC)COC1=CN=C2C(=C(C(=C(C2=N1)Br)F)F)Br |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
5,8-Dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline is a chemical compound that has found its place in the field of organic electronics, particularly in organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices. As an important intermediate material in the design of optoelectronic devices, it has garnered attention for its unique structural properties, which offer potential advantages in various applications. This compound belongs to the quinoxaline family, a class of heterocyclic compounds widely studied for their applications in electronic and optoelectronic materials due to their ability to modulate charge transport and energy levels effectively. The discovery of 5,8-dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline was driven by the desire to enhance the performance of organic materials used in solar cells and other electronic devices. The molecular structure of this compound features key functional groups—bromine and fluorine atoms—located on the quinoxaline backbone, which significantly influence the electronic properties of the material. These halogen atoms contribute to an enhanced electronic conjugation, altering the compound's bandgap and making it suitable for use in high-efficiency organic photovoltaics. The introduction of a long alkyl chain, specifically a 2-hexyldecyl group, in the structure of 5,8-dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline plays a crucial role in modifying the solubility and film-forming properties of the compound. This alkyl group aids in the processing of the material, enabling the fabrication of thin films with favorable morphology for use in OPVs. The solubility improvement is essential for the solution-based processing techniques used in the fabrication of organic solar cells, such as spin-coating or inkjet printing, allowing for scalable production of devices. In terms of applications, 5,8-dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline has shown promise in the development of non-fullerene organic solar cells (NF-OPVs), where its role as an electron acceptor material has been particularly noted. The compound's ability to accept electrons from a donor polymer, coupled with its favorable energy levels and high charge mobility, contributes to improved power conversion efficiencies (PCE) in photovoltaic devices. It also provides better stability compared to traditional fullerene-based acceptors, which is critical for the longevity of solar cells. Furthermore, this compound's distinctive halogenated structure enhances the overall optoelectronic properties, such as light absorption, charge separation, and transport. This allows for the creation of more efficient organic solar cells, with higher PCEs and better operational stability under real-world conditions. In combination with donor polymers, such as PBDB-T or PTB7-Th, this quinoxaline derivative can help optimize the overall efficiency of organic photovoltaic devices. Despite its promising potential, challenges remain in optimizing the processing conditions and scaling up the production of 5,8-dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline for commercial applications. Researchers continue to explore ways to enhance the molecular design, improve the performance of devices, and reduce the cost of synthesis to make it viable for large-scale manufacturing. In summary, 5,8-dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline represents a significant advancement in organic electronics, particularly in the field of organic photovoltaics. Its unique structure and functional groups enable it to contribute to the development of high-efficiency, stable, and scalable solar cells, making it a valuable compound for future renewable energy technologies. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5,8-Dibromo-6,7-difluoro-2-((2-hexyldecyl)oxy)quinoxaline |