Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Inorganic chemical industry >> Inorganic salt >> Hydride, nitride, azide |
|---|---|
| Name | Neodymium nitride |
| Synonyms | azanylidyneneodymium |
| Molecular Structure | 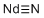 |
| Molecular Formula | NNd |
| Molecular Weight | 158.25 |
| CAS Registry Number | 25764-11-8 |
| EC Number | 247-246-7 |
| SMILES | N#[Nd] |
| SDS | Available |
|---|---|
|
Neodymium nitride (NdN) represents a key advance in the field of magnetic materials, having been synthesized initially through careful research aimed at discovering new magnetic materials. The compound is derived from neodymium, a rare earth element known for its strong magnetic properties, and nitrogen, which brings stability and a unique electronic structure to the material. The synthesis involves reacting neodymium metal with nitrogen gas under controlled conditions, followed by a purification step to obtain the desired crystal structure. Neodymium nitride exhibits superior magnetic properties beyond those of conventional magnetic materials: it has a high atomic magnetic moment, making it ideal for applications requiring strong magnetic fields, such as magnetic storage devices and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. Unlike other magnetic materials, neodymium nitride retains its magnetism at high temperatures, expanding its usefulness in high-temperature environments and industrial applications. The applications of neodymium nitride cover several key areas: it is used to produce high-performance permanent magnets, especially in applications that require compact size and strong magnetic fields, such as electric motors for hybrid and electric vehicles; neodymium nitride plays an important role in advancing magnetic recording technology, increasing the density and efficiency of data storage in hard drives and magnetic tapes; the magnetic properties of neodymium nitride are exploited in biomedical imaging technology, helping to develop more sensitive and precise MRI machines for medical diagnosis. While neodymium nitride has significant technological advantages, its production and use require careful consideration of environmental and economic factors. Neodymium is a rare earth element with limited global reserves, and sustainable mining and recycling practices are required to minimize environmental impact and ensure long-term availability for technological applications. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Neodymium nitride |