Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Wuhan Kemi-works Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (27) 8573-6489 | |||
 |
info@kemiworks.net sales@kemiworks.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Classification | Catalysts and additives >> Polyethylene glycol derivative |
|---|---|
| Name | Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate |
| Molecular Structure | 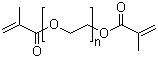 |
| Molecular Formula | (C4H5O).(C2H4O)n.(C4H5O2) |
| CAS Registry Number | 25852-47-5 |
| EC Number | 607-819-8 |
| SMILES | CC(=C)C(=O)OCCOCCOCCOCCOC(=O)C(=C)C |
| Solubility | Soluble (water) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.11 g/mL (25 ºC) |
| Boiling point | >200 ºC (2 mmHg) |
| Refractive index | n20/D 1.467 |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate is a versatile chemical compound known for its unique properties and wide range of applications in various fields, including materials science, medicine, and polymer chemistry. This substance, often abbreviated as PEG-DMA, is a crosslinking agent used extensively in the synthesis of hydrogels and other polymeric materials. The discovery of poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate can be attributed to ongoing research aimed at improving polymer crosslinking methods. Scientists sought to develop a compound that could enhance the properties of polymers by providing efficient crosslinking while maintaining biocompatibility and solubility. PEG-DMA emerged as a valuable material due to its ability to form highly crosslinked networks when polymerized, which significantly alters the physical and chemical properties of the resulting materials. One of the primary applications of poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate is in the formation of hydrogels. These hydrogels are three-dimensional, hydrophilic polymer networks that can absorb and retain large amounts of water. PEG-DMA is used as a crosslinker in the synthesis of these hydrogels, contributing to their mechanical strength, elasticity, and swelling behavior. Due to these properties, PEG-DMA-based hydrogels find extensive use in biomedical applications, such as tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and wound healing. In tissue engineering, PEG-DMA-based hydrogels are utilized as scaffolds that provide a supportive environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration. The hydrophilic nature of the hydrogels, combined with their biocompatibility, makes them ideal for creating environments that mimic natural tissues. This application is crucial for developing advanced medical treatments and regenerative therapies. PEG-DMA is also used in the development of controlled drug release systems. The hydrogels formed with PEG-DMA can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner over time. This property is beneficial for creating drug delivery systems that provide sustained and targeted release, improving the efficacy of treatments and reducing side effects. In addition to its applications in medicine, poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate is employed in the field of materials science for creating advanced polymeric materials. The compound is used to produce coatings, adhesives, and composites with enhanced properties, such as improved mechanical strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. These materials are utilized in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The research into poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate continues to explore new applications and improvements in its synthesis and functionality. Scientists are investigating ways to modify PEG-DMA to achieve specific properties and enhance its performance in various applications. This ongoing research aims to expand the use of PEG-DMA in both existing and emerging fields. In summary, poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate is a significant chemical compound with a range of applications in hydrogels, drug delivery systems, and advanced materials. Its ability to crosslink polymers and form hydrophilic networks makes it a valuable substance in both biomedical and industrial contexts. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate |