Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hengshui Haoye Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (318) 210-2300 +86 18632882519 | |||
 |
firmcn@gmail.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Aajiang Jiuzhou Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13454675544 | |||
 |
jamie@jiuzhou-chem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: +86 18632988332 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 18632988332 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Yusweet Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0532) 8563-0138 | |||
 |
sales@ayyuxin.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1996 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Shanghai Etangtechnology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 15216896005 | |||
 |
heidi.fu@etangtech.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 15216896005 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 0086 15216896005 | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2025 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Carbone Scientific Co., Ltd. | UK | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+44 (870) 486-8629 | |||
 |
sales@carbonesci.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| Omicron Biochemicals, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (574) 287-6910 | |||
 |
omicron@omicronbio.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Carbohydrate >> Monosaccharide |
|---|---|
| Name | D-Psicose |
| Synonyms | D-Allulose; D-ribo-2-Hexulose |
| Molecular Structure | 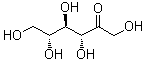 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 551-68-8 |
| EC Number | 208-999-7 |
| SMILES | C([C@H]([C@H]([C@H](C(=O)CO)O)O)O)O |
| Solubility | Freely soluble (160 g/L) (25 ºC), Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.589±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr), Calc.* |
| Melting point | 162 ºC (ethanol )** |
| Index of refraction | 1.574, Calc.* |
| Boiling point | 551.7±50.0 ºC 760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash point | 301.5±26.6 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software V11.02 (©1994-2014 ACD/Labs) |
| ** | Khouvine, Yvonne; Compt. rend. 1937, V205, P736-8. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
D-Psicose, also known as allulose, is a monosaccharide that belongs to the class of rare sugars. Its chemical structure is similar to that of fructose, with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Despite being chemically similar to glucose and fructose, D-psicose is unique due to its distinct physiological properties. It was first discovered in the 1940s, but its potential applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries have only gained significant attention in recent years. D-Psicose is naturally found in small amounts in various fruits and foods, including figs, raisins, and maple syrup. However, it is not present in high enough concentrations to be harvested directly from natural sources in quantities suitable for commercial use. Instead, D-psicose is typically produced through enzymatic conversion of fructose using specific enzymes such as D-psicose 3-epimerase. This process allows for the large-scale production of D-psicose, making it available for use in a variety of industries. One of the most notable properties of D-psicose is its ability to provide a sweet taste without significantly affecting blood sugar levels. This has made it an attractive alternative to traditional sugars, especially for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to reduce their calorie intake. D-Psicose is approximately 70% as sweet as sucrose, but it is absorbed more slowly by the body and has a minimal effect on blood glucose and insulin levels. This makes it a potential sugar substitute in food products aimed at health-conscious consumers and those with metabolic conditions. In addition to its use as a sugar substitute, D-psicose has also been explored for its potential health benefits. Research has shown that it may help in weight management by reducing fat accumulation and improving lipid metabolism. It has also been studied for its potential to improve insulin sensitivity, making it a promising candidate for managing metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, D-psicose is considered safe for consumption and has been granted Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Another area where D-psicose is gaining attention is in the field of food preservation. Due to its low glycemic index and unique sweetness profile, it is being used as a sweetener in various food products, including beverages, dairy products, baked goods, and confectioneries. It is particularly useful in products marketed as low-calorie or diabetic-friendly alternatives. In addition, D-psicose’s ability to prevent the crystallization of sugar in food formulations can improve the texture and mouthfeel of certain products. D-Psicose is also being studied for its potential role in gut health. Some studies have suggested that it may act as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This could lead to improvements in digestive health and overall well-being, further expanding the potential applications of this sugar in the functional food sector. Despite its promising applications, D-psicose is still relatively new to the market, and ongoing research is necessary to fully understand its long-term effects on health and its full range of applications. As more studies are conducted, it is likely that new uses for D-psicose will emerge, further solidifying its role as a versatile and beneficial sugar substitute. References 1948. Acetylation of D-Psicose. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 70(11). DOI: 10.1021/ja01191a505 2024. Production, purification, characterization, and safety evaluation of constructed recombinant D-psicose 3-epimerase. Microbial Cell Factories, 23(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02487-x 2024. Optimization and Comparative Methods for Efficient D-psicose Production Using Physicochemical and Enzymatic Processes. Sugar Tech, 26(4). DOI: 10.1007/s12355-024-01423-y |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for D-Psicose |