Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Zhangjiagang For Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5679-6585 5897-6331 | |||
 |
info@forchemical.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Zhangjiagang Huachang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5818-5820 +86 13812985197 | |||
 |
huachangpharm@163.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Jiangsu B-Win Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (510) 8584-0252 +86 18861806888 | |||
 |
huisongshu_2001@163.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| NPA Laboratories, LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (714) 656-3915 | |||
 |
info@npalab.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Extrasynthese Chemical S.A.S. | France | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+33 (47) 898-2034 | |||
 |
info@extrasynthese.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Common amino acids and protein drugs |
|---|---|
| Name | L-Serine |
| Synonyms | L-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropionic acid; 3-Hydroxy-alanine; Ser |
| Molecular Structure | 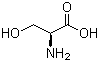 |
| Protein Sequence | S |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 105.09 |
| CAS Registry Number | 56-45-1 |
| EC Number | 200-274-3 |
| SMILES | C([C@@H](C(=O)O)N)O |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.537 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 222 ºC (Decomposes) (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 394.8±32.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 192.6±25.1 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.519 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
L-Serine is a naturally occurring, proteinogenic α-amino acid with the chemical formula HOCH2CH(NH2)COOH. It is classified as a polar, uncharged amino acid due to the presence of a hydroxymethyl side chain. L-Serine is one of the 20 standard amino acids encoded by the universal genetic code and plays a vital role in the biosynthesis of proteins in all forms of life. The discovery of L-serine dates back to 1865 when it was first isolated from silk protein, which is particularly rich in this amino acid. Its name derives from "sericum," the Latin word for silk. The elucidation of its chemical structure and stereochemistry in the early 20th century helped establish the broader understanding of amino acid behavior, protein composition, and enzymatic specificity. In biological systems, L-serine is synthesized endogenously via the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate. The biosynthetic pathway involves three enzymatic steps: oxidation to 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate, transamination to 3-phosphoserine, and dephosphorylation to produce L-serine. These reactions occur predominantly in the cytosol and are tightly regulated to maintain cellular serine homeostasis. L-Serine serves as a metabolic precursor to several essential biomolecules. It is a key contributor to the synthesis of nucleotides, phospholipids, and sphingolipids. Through conversion to glycine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase, it donates one-carbon units for the folate-mediated one-carbon metabolism pathway, which is crucial for DNA and RNA synthesis. In phospholipid biosynthesis, L-serine is the backbone for phosphatidylserine, a major component of eukaryotic cell membranes involved in cell signaling and apoptosis. In the central nervous system, L-serine and its derivative D-serine have distinct functions. While L-serine is synthesized by astrocytes and supports neuronal function, D-serine, formed by racemization of L-serine, acts as a co-agonist at the NMDA-type glutamate receptor, influencing synaptic plasticity and neurotransmission. This duality underscores the importance of stereochemical form in biological activity. L-Serine also plays a role in the detoxification of homocysteine via the transsulfuration pathway and contributes to the production of cysteine. Moreover, it is a substrate for the synthesis of tryptophan and purines, making it central to several metabolic networks. In applied sciences, L-serine is utilized in the pharmaceutical and food industries. It is a component of parenteral nutrition formulations and cell culture media, supporting the growth and maintenance of mammalian cells in vitro. It also serves as a chiral building block in asymmetric synthesis and as an intermediate in the production of certain active pharmaceutical ingredients, particularly those involving hydroxylated side chains. Deficiencies or imbalances in L-serine metabolism are associated with neurological disorders, including hereditary serine deficiency syndromes such as 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency. These conditions can lead to severe developmental delays, microcephaly, and seizures, which are treatable to some extent by dietary supplementation with L-serine. L-Serine’s combination of structural simplicity and functional diversity makes it indispensable in both fundamental biochemistry and applied biomedical research. It is a key node in metabolism, serving as both a building block and a regulator in numerous biochemical pathways. References 2021. Metabolic Changes in Brain Slices over Time: a Multiplatform Metabolomics Approach. Molecular Neurobiology, 58(6). DOI: 10.1007/s12035-020-02264-y 2021. Time-course analysis of Streptococcus sanguinis after manganese depletion reveals changes in glycolytic and nucleic acid metabolites. Metabolomics: Official journal of the Metabolomic Society, 17(5). DOI: 10.1007/s11306-021-01795-2 2021. 3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase: a potential target for cancer treatment. Cellular oncology (Dordrecht, Netherlands), 44(3). DOI: 10.1007/s13402-021-00599-9 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for L-Serine |