Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Langfang GreatAp Chemicals Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (316) 209-8955 +86 18630626679 | |||
 |
sales@grechembld.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Jiangsu Raien Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 16651336278 | |||
 |
1780189359@qq.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2015 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Saian Chemical (shanghai) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18633110822 | |||
 |
teresa.liu@saianchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 18633110822 | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2018 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Inorganic chemical industry >> Inorganic salt >> Hydride, nitride, azide >> Hydride |
|---|---|
| Name | Magnesium hydride |
| Synonyms | Magnesium dihydride; Magnesium hydride; Tego Magnan |
| Molecular Structure | 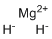 |
| Molecular Formula | MgH2 |
| Molecular Weight | 26.32 |
| CAS Registry Number | 7693-27-8 |
| EC Number | 231-705-3 |
| SMILES | [H-].[H-].[Mg+2] |
| Melting point | >250 ºC (decomp)* |
|---|---|
| Refractive index | 1.94 (589.3 nm)** |
| * | """"Metal-Organics Catalog"""" physical property data were obtained from Gelest, Inc. of Morrisville, Pennsylvania (US) |
| ** | Isidorsson, J.; Los Alamos National Laboratory, Preprint Archive, Condensed Matter 2003, P1-15, arXiv:cond-mat/0305418. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS02;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H228-H260-H315-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P223-P231+P232-P240-P241-P264-P264+P265-P280-P302+P335+P334-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P402+P404-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2010 4.3 / PGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Magnesium hydride (MgH₂) is a compound with unique properties that have great potential for application in various fields of technology. Discovered in the early 20th century, MgH₂ stands out for its ability to store hydrogen, making it an ideal material for energy storage and other applications. The first synthesis of MgH₂ dates back to 1918 by chemist L. R. McCarty, who observed that magnesium could react with hydrogen under certain conditions to form MgH₂. Early research focused on understanding its physical and chemical properties, and found that MgH₂ is a white crystalline solid that releases hydrogen when heated. MgH₂ is characterized by its high hydrogen storage capacity, which can hold up to 7.6 wt% (weight percent) of hydrogen. This property stems from its ability to reversibly absorb and release hydrogen, making it a key candidate for hydrogen storage technology. In addition, MgH₂ is relatively low in cost and highly available, as magnesium is one of the most abundant metals on Earth. The most notable application of MgH₂ is in hydrogen storage systems. Due to its high hydrogen density and reversibility, it is used in fuel cell vehicles and portable power sources. Researchers are developing advanced storage systems that utilize magnesium hydride to improve the efficiency and safety of hydrogen storage. Magnesium hydride is also used as a catalyst for various chemical reactions. Its ability to release hydrogen makes it useful in hydrogenation reactions, facilitating the addition of hydrogen to organic compounds, thereby enhancing the production of fuels and chemicals. In thermal applications, magnesium hydride's hydrogen-releasing properties can be used for cooling and thermal regulation. Its endothermic reaction during hydrogen absorption can be used in thermal management systems to regulate the temperature of electronic devices and other heat-sensitive devices. Ongoing research aims to improve the efficiency and usefulness of magnesium hydride for a wider range of applications. Innovations in materials science and nanotechnology focus on improving the kinetics of hydrogen absorption and desorption, as well as reducing the energy required for these processes. As the technology continues to advance, magnesium hydride may play a key role in sustainable energy solutions and industrial applications. References Feiwu Zhang, Andrew M. Walker, Kate Wright and Julian D. Gale. Defects and dislocations in MgO: atomic scale models of impurity segregation and fast pipe diffusion, J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 10445. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Magnesium hydride |