Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Nanjing Finetech Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 5207-8417 +86 17714198479 | |||
 |
sales@fine-chemtech.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Sinfachem Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8468-3399 8517-8591 | |||
 |
sinfachem@foxmail.com sinfachemltd@foxmail.com info@sinfachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Joyochem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13290333633 | |||
 |
sales@joyochem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13290333633 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyran compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 5,7-Difluorochroman-4-one |
| Synonyms | 5,7-Difluoro-2,3-dihydro-4H-chromen-4-one; 5,7-Difluoro-3,4-dihydro-4H-chromen-4-one |
| Molecular Structure | 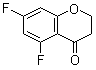 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H6F2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 184.14 |
| CAS Registry Number | 844648-22-2 |
| SMILES | C1COC2=C(C1=O)C(=CC(=C2)F)F |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 282.9±40.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 121.1±22.2 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.519 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H332-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
5,7-Difluorochroman-4-one is a fluorinated chromanone derivative, characterized by a chroman-4-one core with fluorine substituents at the 5- and 7-positions of the aromatic ring. Chroman-4-one compounds are important scaffolds in medicinal chemistry and material science due to their biological activity and chemical versatility. The introduction of fluorine atoms enhances the compound’s chemical stability, lipophilicity, and metabolic resistance, which are advantageous properties for pharmaceutical applications. The discovery of 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one is rooted in the broader exploration of fluorinated chromanone derivatives, which began in the late 20th century as researchers investigated the effects of fluorination on biological activity and pharmacokinetic properties. Fluorinated chromanones have been synthesized to study their potential as enzyme inhibitors, antioxidants, and bioactive agents in the treatment of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and inflammatory diseases. The specific 5,7-difluoro substitution pattern was found to influence the electronic distribution and molecular conformation, which can enhance interactions with biological targets. In chemical synthesis, 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one can be prepared through cyclization reactions of appropriately substituted hydroxyaryl ketones or through condensation of fluorinated phenols with α-haloketones. The presence of fluorine atoms requires careful selection of reaction conditions to avoid dehalogenation or side reactions, often employing mild bases, aprotic solvents, and controlled temperatures. The resulting product is typically purified by crystallization or chromatography and characterized by NMR, mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis to confirm the substitution pattern and purity. The applications of 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one are mainly in medicinal chemistry research, where it serves as a building block for the synthesis of biologically active compounds. Its fluorinated chromanone structure can be further modified to create derivatives that act as selective enzyme inhibitors, antioxidants, or receptor modulators. In drug design, fluorine atoms often improve binding affinity, metabolic stability, and bioavailability, making 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one a valuable intermediate for the development of novel therapeutics. In addition to pharmaceutical research, 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one may be utilized in material science studies, such as in the development of fluorescent probes or organic semiconductors, where the chromanone framework and fluorine substitution contribute to favorable electronic properties. Its chemical stability and rigidity make it suitable for incorporation into conjugated systems, providing potential applications in optoelectronic devices. Overall, 5,7-difluorochroman-4-one represents a versatile fluorinated chromanone scaffold with utility in both medicinal chemistry and materials science. Its synthetic accessibility, stability, and functionalization potential enable the exploration of structure-activity relationships and the development of novel compounds with enhanced biological or electronic properties. The combination of fluorination and the chroman-4-one core makes it a valuable intermediate for advanced chemical research. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5,7-Difluorochroman-4-one |