Epichlorohydrin (ECH) is an organochlorine compound with the molecular formula C3H5ClO. It was first synthesized by the French chemist Charles Adolphe Wurtz in 1850. Due to the presence of both an epoxy ring and a chlorine atom, ECH is a highly reactive compound and a valuable intermediate in the production of various industrial chemicals.
Epichlorohydrin is a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It is slightly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. ECH has a boiling point of 116°C and a density of 1.18 g/cm³ at 25°C. The reactivity of the molecule stems from its strained three-membered epoxy ring and the electron-withdrawing effect of the chlorine atom.
One of the main uses of epichlorohydrin is in the production of epoxy resins: ECH reacts with bisphenol A to form diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA), the main component of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins are widely used in coatings, adhesives, and composites due to their excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and strong adhesion.
Epichlorohydrin is used as an intermediate in the synthesis of glycerol: ECH hydrolyzes to produce glycerol, a valuable compound in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. Glycerol can be used as a humectant, solvent, and sweetener, among other things.
ECH is used in the production of synthetic rubbers and elastomers: Epichlorohydrin rubber has good resistance to oils, fuels, and ozone. Due to its durability and flexibility, it is used in automotive seals, hoses, and fuel system components.
Epichlorohydrin is a key ingredient in the manufacture of water treatment chemicals: ECH is used to produce anion exchange resins, which are essential in the water purification process. These resins remove contaminants such as nitrates, sulfates, and organic acids from water.
ECH is a building block for the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds: It is used as an intermediate in the preparation of a wide range of drugs, including antibiotics and other active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its reactivity allows the introduction of complex molecular structures.
Epichlorohydrin is used in the production of certain agrochemicals: Epichlorohydrin is an intermediate in the synthesis of certain insecticides and fungicides, which helps in the development of effective agrochemicals to protect crops from pests and diseases.
Epichlorohydrin is a hazardous substance and must be handled with care. It is toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. Long-term exposure can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, and may be carcinogenic. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), ventilation, and safety procedures are essential to minimize health risks when working with epichlorohydrin.
The production and use of epichlorohydrin can have an impact on the environment, especially if released into the environment. It is important to manage and mitigate its release through proper control, handling, and disposal methods. Regulatory measures must be in place to ensure safe handling and minimize its impact on the environment.
|

















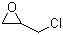




 GHS02;GHS06;GHS07;GHS08;GHS05 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS06;GHS07;GHS08;GHS05 Danger Details