Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Amadis Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8992-5085 | |||
 |
sales@amadischem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Shanghai CR Corporation Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 5736-6208 +86 13917420128 | |||
 |
fred.wen@crcorporation.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Changzhou Jiuwu Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8512-1086 +86 13775162768 | |||
 |
info@jiuwuchem.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (831) 457-3800 | |||
 |
scbt@scbt.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Anvia Chemicals, LLC | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (414) 534-7845 | |||
 |
sales@anviachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| ECA International Corporation | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (847) 358-8178 | |||
 |
order@ecacorporation.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Methyl ester compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate |
| Molecular Structure | 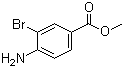 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8BrNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 230.06 |
| CAS Registry Number | 106896-49-5 |
| EC Number | 628-549-7 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1=CC(=C(C=C1)N)Br |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 104-108 ºC (Expl.) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 334.2±22.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash Point | 155.9±22.3 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H301-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P264+P265-P270-P280-P301+P316-P305+P351+P338-P321-P330-P337+P317-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2811 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate is an aromatic compound that features a bromine atom, an amino group, and an ester functional group attached to a benzene ring. This multifunctional compound is widely used in organic synthesis due to its reactivity and structural versatility. It plays a crucial role in the development of advanced materials, pharmaceutical intermediates, and dyes. The synthesis of methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate typically begins with the bromination of methyl 4-aminobenzoate. This process introduces a bromine atom at the meta position relative to the amino group. Brominating agents such as bromine in acetic acid or N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) are commonly used to achieve high selectivity. Alternative synthesis routes involve functional group transformations starting from appropriately substituted benzoates. Methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate serves as a key intermediate in pharmaceutical research, particularly in the production of bioactive molecules. The bromine atom allows for further functionalization through cross-coupling reactions, such as Suzuki-Miyaura or Buchwald-Hartwig coupling. These reactions enable the incorporation of diverse substituents, facilitating the development of compounds with specific therapeutic properties. Additionally, the amino group can be modified through acylation or alkylation, expanding the compound's utility in drug discovery. In the field of materials science, methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate is used as a precursor for synthesizing advanced polymers and functional materials. The compound's aromatic core and functional groups contribute to the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and optical properties of the resulting materials. Its applications include coatings, electronic components, and specialty resins. Methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate is also valued in dye chemistry. The combination of an amino group and an aromatic ester facilitates the synthesis of chromophores with specific color properties. These dyes are used in textiles, printing, and analytical applications. Recent research has focused on optimizing the synthesis of methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate through green chemistry methods, such as solvent-free reactions and the use of recyclable catalysts. Additionally, its role in synthesizing novel heterocyclic compounds has expanded its importance in medicinal chemistry and agrochemical development. References 2021. A Practical Procedure for Regioselective Bromination of Anilines. Synthesis. DOI: 10.1055/a-1441-3236 2016. Recent Advances in Bromination of Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Compounds. Synthesis. DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1561503 2014. One-Step Synthesis of Quinolines via Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Cyclopropanols with Unprotected ortho-Bromoanilines. Synlett. DOI: 10.1055/s-0034-1378613 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl 4-amino-3-bromobenzoate |