Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Aromsyn Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8558-5865 +86 13336024896 | |||
 |
service@aromsyn.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Molcore Biopharmatech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8102-5280 | |||
 |
sales@molcore.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Chengdu Yuanda Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (28) 8535-6300 | |||
 |
sales@ydachem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Dynamic International Enterprises Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6231-2607 (510) 8755-1178 8755-4400 | |||
 |
china@dynai.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Georganics Ltd. | Slovakia | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+421 (33) 640-3132 | |||
 |
georganics@georganics.sk | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1998 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Halogenation, sulfonation, nitration or nitration of carboxylic anhydrides |
|---|---|
| Name | 4-Chlorophthalic anhydride |
| Synonyms | 5-chloro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione |
| Molecular Structure | 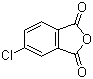 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H3ClO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 182.56 |
| CAS Registry Number | 118-45-6 |
| EC Number | 204-251-9 |
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=C1Cl)C(=O)OC2=O |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 96 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 299.8±13.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 295 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 142.4±18.8 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.627 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H318-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P305+P354+P338-P317-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4-Chlorophthalic anhydride (C8H3ClO3, CAS 118-45-6) is a monochlorinated derivative of phthalic anhydride. It belongs to the family of halogenated aromatic anhydrides, which are important intermediates in the synthesis of high-performance polymers and specialty organic compounds. The compound is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of about 96 °C and a boiling point near 290 °C. It exhibits high reactivity due to the presence of the anhydride group, while the chlorine substituent on the aromatic ring influences both its chemical behavior and its utility in polymer chemistry. The discovery of 4-chlorophthalic anhydride occurred during the systematic study of halogenated phthalic derivatives in the mid-twentieth century. These investigations sought to explore the effect of halogen substitution on the chemical reactivity and physical properties of aromatic anhydrides. Chlorinated phthalic anhydrides were prepared primarily through direct chlorination of phthalic anhydride or by oxidation of chlorinated xylene precursors. The 4-chloro isomer was obtained as one of several positional isomers, alongside the 3-chloro and 5-chloro forms. Among these, the 4-chloro compound displayed favorable properties for controlled polymer synthesis and became the preferred derivative for certain industrial applications. In laboratory and industrial synthesis, 4-chlorophthalic anhydride is commonly prepared by the chlorination of phthalic anhydride using chlorine gas or sulfuryl chloride under controlled conditions. An alternative route involves oxidation of 4-chloro-o-xylene or 4-chlorophthalic acid. The anhydride can also be formed by dehydration of 4-chlorophthalic acid using acetic anhydride or other dehydrating agents. These methods yield a high-purity product suitable for further transformation in polymer or fine chemical production. The principal application of 4-chlorophthalic anhydride lies in the synthesis of polyimides and related high-performance polymers. It functions as a monomer or comonomer in condensation reactions with diamines to form imide linkages, resulting in materials with excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Polyimides derived from chlorinated phthalic anhydrides show enhanced solubility and improved processability compared with those derived from unsubstituted phthalic anhydride. The chlorine atom in the aromatic ring contributes to altered electronic properties and can participate in subsequent substitution or coupling reactions, providing a route to functionalized or cross-linked polymer systems. Another important use of 4-chlorophthalic anhydride is in the preparation of specialty curing agents and intermediates for epoxy resins. The compound reacts with alcohols, amines, or phenols to yield esters, amides, and imides that serve as hardeners or modifiers in high-performance coatings and adhesives. Its halogenated nature provides thermal resistance and improved adhesion characteristics. Additionally, it has been utilized as a building block for the synthesis of dianhydrides that are used in advanced polymer networks such as polyetherimides and poly(amic acid) precursors. In industrial practice, 4-chlorophthalic anhydride is also used in the manufacture of certain pigments, dyes, and agrochemical intermediates. The aromatic ring with an electron-withdrawing chlorine substituent offers a convenient platform for further substitution or condensation reactions, expanding its value as a versatile intermediate. Studies on the phase behavior and solid–liquid equilibrium of the compound, including its mixtures with 3-chlorophthalic anhydride, have provided data important for optimizing crystallization and purification processes in industrial production. Overall, 4-chlorophthalic anhydride represents an important chemical intermediate whose discovery was linked to the development of halogenated aromatic anhydrides and their applications in polymer chemistry. Its ability to introduce both reactivity and stability into polymer systems has made it a preferred precursor for materials that must perform under high thermal and chemical stress. Continued research into its properties and derivatives supports its role in the production of specialty polymers and high-performance materials. References 2024. Crosslinked Colorless Polyimide Films via Oxazole Groups as Crosslinking Agent: Preparation and Properties. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science. DOI: 10.1007/s10118-024-3235-0 2015. Solubility and Dissolution Thermodynamic Properties of 3,3',4,4'-Oxydiphthalic Anhydride in Binary Aqueous Solutions of Acetic Acid and Propionic Acid from (278.15 to 313.15) K. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 44(10). DOI: 10.1007/s10953-015-0388-z 2015. Synthesis and characterization of high performance poly(thioether imide)s via aromatic nucleophilic substitution reaction of isomeric AB-type monomers. Polymer Bulletin, 72(11). DOI: 10.1007/s00289-015-1465-6 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 4-Chlorophthalic anhydride |