Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Rui Yun Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6726-7633 | |||
 |
sales@rychemical.com.cn | |||
 |
WeChat: 13917251563 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Halogenation, sulfonation, nitration or nitrosation of carboxylic acids |
|---|---|
| Name | 4-Bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 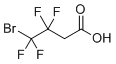 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H3BrF4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 238.96 |
| CAS Registry Number | 131118-43-9 |
| SMILES | C(C(=O)O)C(C(F)(F)Br)(F)F |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H332 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P301+P317-P302+P352-P304+P340-P317-P321-P330-P362+P364-P501 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
4-Bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid is an organofluorine compound known for its distinct combination of bromine and fluorine atoms within a butanoic acid structure. This molecule features a butanoic acid backbone, with two pairs of fluorine atoms and a bromine atom attached to the carbon chain. The presence of both halogens in the structure imparts the compound with unique chemical reactivity, making it useful in several applications in organic synthesis and material sciences. The discovery of 4-bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid is linked to developments in the field of fluorine chemistry. Researchers aimed to produce molecules that incorporate both bromine and fluorine due to their contrasting yet complementary properties. Fluorine provides thermal stability and resistance to degradation, while bromine allows for functionalization and further chemical modifications. The structure of this compound enables its use as a precursor or intermediate in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules, especially in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries. One of the key applications of 4-bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid is in the preparation of fluorinated building blocks. The presence of fluorine atoms can significantly alter the biological activity of molecules, making fluorinated derivatives critical in drug design and development. This compound serves as a useful starting material for synthesizing various fluorinated pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals that require both fluorine for metabolic stability and bromine for selective reactivity. In addition to its role in organic synthesis, 4-bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid has applications in material science. The fluorinated portion of the molecule imparts hydrophobic and lipophobic properties, making it suitable for use in coatings and polymers where water and oil repellency are desirable. It also finds use in specialty materials, such as fluorinated elastomers and high-performance polymers, due to the chemical stability introduced by fluorine atoms. The dual nature of 4-bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid—combining bromine's reactivity with fluorine's stability—makes it a versatile compound for various applications in modern chemistry. As research continues to explore the potential of fluorinated materials, this compound will likely play a role in future innovations. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 4-Bromo-4,4,3,3-tetrafluorobutanoic acid |