Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Jinan Chenghui-Shuangda Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (531) 5889-7051 +86 15053146086 | |||
 |
jnchsd@qq.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Changzhou Sunchem Pharmaceutical Chemical Material Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8519-5575 8519-5528 8519-5565 | |||
 |
info@sunkechem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Shanghai Hohance Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3111-5312 | |||
 |
info@hohance.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (531) 8811-0457 | |||
 |
happy@pharmachemm.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2011 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Wuhan Demeikai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 +86 (027) 5045-8986 +86 17192727886 | |||
 |
sare@dmksw.xin wzh@dmksw.xin | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Anesthetic agents >> Local anesthetics |
|---|---|
| Name | Lidocaine |
| Synonyms | 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide; Xylocaine |
| Molecular Structure | 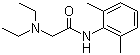 |
| Protein Sequence | G |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 234.34 |
| CAS Registry Number | 137-58-6 |
| EC Number | 205-302-8 |
| SMILES | CCN(CC)CC(=O)NC1=C(C=CC=C1C)C |
| Solubility | 47 mg/mL (DMSO), 9 mg/mL (water) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
| Melting point | 66-69 ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.512, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 372.7±52.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.*, 182 ºC (4 mmHg) |
| Flash Point | 179.2±30.7 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P270-P301+P317-P330-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lidocaine, chemically known as 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide, is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic agent widely used in medical practice. Its discovery dates back to the late 1940s when it was first synthesized by Swedish chemist Nils Löfgren. Lidocaine was developed as a safer and more effective alternative to procaine, the then-popular local anesthetic. The introduction of lidocaine marked a significant advancement in the field of anesthesia due to its rapid onset of action and relatively short duration compared to earlier anesthetics. Lidocaine acts by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. This mechanism of action is fundamental to its effectiveness as a local anesthetic. When administered locally, lidocaine provides anesthesia to a specific area, allowing for various medical and dental procedures to be performed without pain. The compound is available in several formulations, including injectable solutions, topical creams, and gels, making it versatile for various clinical applications. The applications of lidocaine extend beyond local anesthesia. It is commonly used in dental procedures, minor surgical interventions, and various dermatological treatments. Its efficacy in alleviating pain during these procedures has made it a staple in healthcare settings. Furthermore, lidocaine is utilized in the treatment of certain cardiac arrhythmias, particularly ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, where it helps stabilize the cardiac membrane and restore normal rhythm. In addition to its established uses, lidocaine has found applications in pain management strategies. Its topical formulations are often employed for conditions such as postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and other chronic pain syndromes. The ability to deliver lidocaine directly to the site of pain through topical administration provides patients with effective pain relief while minimizing systemic exposure. The discovery of lidocaine has also paved the way for further research into the development of new local anesthetics and modifications of existing compounds. Researchers have explored various derivatives of lidocaine to enhance its potency, duration of action, and safety profile. These advancements contribute to ongoing efforts to improve patient care and comfort during medical procedures. Despite its widespread use, lidocaine is not without risks. Adverse effects may include allergic reactions, cardiovascular complications, and central nervous system toxicity, particularly when administered inappropriately or in excessive doses. Therefore, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring patients during and after lidocaine administration to ensure safety and efficacy. In summary, lidocaine stands as a cornerstone in the field of local anesthesia and pain management, owing to its rapid onset, effectiveness, and versatility. From its discovery in the 1940s to its current applications in various medical fields, lidocaine has significantly impacted patient care by providing effective pain relief and contributing to the safety of surgical and medical interventions. References 1979. Penetration Enhancers and Other Factors Governing Percutaneous Local Anaesthesia with Lidocaine. Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica, 45(1). DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1979.tb02361.x 1979. Therapeutic Blood Lidocaine Concentrations after Local Anesthesia for Cardiac Electrophysiologic Studies. The New England Journal of Medicine, 301(8). DOI: 10.1056/nejm197908233010808 1979. Cytotoxic Effects of Procaine, Lignocaine and Bupivacaine. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 51(4). DOI: 10.1093/bja/51.4.273 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Lidocaine |