Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| SL Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (40) 6661-1133 | |||
 |
enquiry@sldrugs.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 1999 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Biosynth AG. | Switzerland | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+41 (71) 858-2020 | |||
 |
welcome@biosynth.ch | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Shanghai Qinba Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6517-0832 +86 17301729617 | |||
 |
shangfluoro@hotmail.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2011 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Wonderchem Co., Limited | Hong Kong | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+852 8192-5218 | |||
 |
sales@wonder-chem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2017 | ||||
| Neostar United (Changzhou) Industrial Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8555-7386 +86 18015025600 | |||
 |
marketing1@neostarunited.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2014 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2020 | ||||
| Sifluorotm Co,. Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0531) 8590-6692 | |||
 |
inquiry@fluoro.com | |||
 |
WeChat: 15288857388 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Indofine Chemical Company, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (888) 463-6346 | |||
 |
info@indofinechemical.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1981 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Methyl ester compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl chlorodifluoroacetate |
| Synonyms | Methyl 2-chloro-2,2-difluoroacetate |
| Molecular Structure | 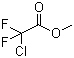 |
| Molecular Formula | C3H3ClF2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 144.50 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1514-87-0 |
| EC Number | 216-154-9 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)C(F)(F)Cl |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.*, 1.371 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Index of Refraction | 1.359, Calc.*, 1.349 (Expl.) |
| Boiling Point | 80.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.*, 79-81 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash Point | 19.4 ºC, Calc.*, 19 ºC (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS02;GHS05 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H225-H314 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P321-P363-P370+P378-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 2924 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyl chlorodifluoroacetate (C3H3ClF2O2) is a fluorinated organic compound that serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of various fluorinated materials. It is structurally characterized by the presence of a chlorodifluoromethyl (-CF2Cl) group attached to an ester functional group, which influences its reactivity and physicochemical properties. The synthesis of methyl chlorodifluoroacetate has been documented in the literature, typically involving the reaction of chlorodifluoroacetic acid or its derivatives with methanol in the presence of an acid catalyst. Alternatively, fluorination strategies employing chlorodifluoromethylation reagents allow for its formation under controlled conditions. The resulting ester is a stable compound with a reactive halogenated center, making it useful for further transformations. Methyl chlorodifluoroacetate finds applications as a precursor in the production of fluorinated pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty materials. The presence of the -CF2Cl group enhances the metabolic stability and lipophilicity of derived compounds, properties that are often desirable in drug discovery and pesticide development. This compound is also utilized in fluorinated polymer synthesis, where its reactivity enables the incorporation of halogenated moieties into high-performance materials. In organic synthesis, methyl chlorodifluoroacetate serves as an electrophilic reagent for introducing the chlorodifluoromethyl functionality into complex molecules. The ester group allows for hydrolysis, transesterification, and nucleophilic substitution reactions, expanding its synthetic utility. Additionally, the halogenated carbon center can undergo further functionalization through metal-catalyzed coupling reactions, providing access to structurally diverse fluorinated compounds. The handling and storage of methyl chlorodifluoroacetate require appropriate safety precautions due to its potential reactivity and volatility. It should be kept in a sealed container under dry and inert conditions to prevent hydrolysis and decomposition. Exposure to this compound may pose health risks, necessitating the use of personal protective equipment and proper ventilation when working with it in laboratory and industrial settings. The continued demand for fluorinated compounds in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and material sciences ensures the relevance of methyl chlorodifluoroacetate as a valuable synthetic intermediate. Its well-established role in chemical transformations highlights its importance in the development of advanced fluorinated molecules. References 2019. Expanding the 18F-Radiochemical Space: Synthesis and Applications of 1,1-18F-Difluorinated Alkenes. Synlett, 30(10). DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1611764 2014. Electron driven processes in chlorodifluoroacetic acid methyl ester. The European Physical Journal D, 68(7). DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2014-50089-3 2013. A theoretical investigation on the kinetics and reactivity of the gas-phase reactions of ethyl chlorodifluoroacetate with OH radical and Cl atom at 298 K. Structural Chemistry, 24(6). DOI: 10.1007/s11224-013-0312-3 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl chlorodifluoroacetate |