Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Targetmol China | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (400) 820-0310 | |||
 |
sales@targetmol.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2015 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Inhibitor >> Neuronal signaling >> GluR agonist |
|---|---|
| Name | CNS-5161 hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | 2-(2-chloro-5-methylsulfanylphenyl)-1-methyl-1-(3-methylsulfanylphenyl)guanidine;hydrochloride |
| Molecular Structure | 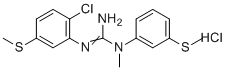 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19Cl2N3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 388.38 |
| CAS Registry Number | 160756-38-7 |
| SMILES | CN(C1=CC(=CC=C1)SC)C(=NC2=C(C=CC(=C2)SC)Cl)N.Cl |
| Solubility | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| SDS | Available |
|---|---|
|
CNS-5161 hydrochloride is a chemical compound that functions as a selective antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor ion channel. The NMDA receptor is a subtype of glutamate receptor found in nerve cells and plays a critical role in synaptic transmission, plasticity, and excitotoxicity in the central nervous system. Overactivation of NMDA receptors is implicated in various neurological conditions such as neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. The discovery of CNS-5161 hydrochloride arose from efforts to develop NMDA receptor antagonists that could selectively inhibit receptor function without causing widespread neurological side effects. The compound is a noncompetitive antagonist, meaning it binds to the NMDA receptor ion channel at a site distinct from the glutamate binding site, blocking the flow of ions such as calcium through the channel. This mechanism reduces excessive neuronal excitability and protects neurons from excitotoxic damage caused by high glutamate levels. CNS-5161 hydrochloride has been studied extensively in preclinical models. Its selectivity for the NMDA receptor ion channel makes it a valuable tool in neuropharmacological research to investigate the role of NMDA receptors in normal and pathological brain function. Experimental studies have demonstrated that CNS-5161 can reduce neuronal damage in models of ischemia and neurodegeneration, as well as modulate neuropathic pain by inhibiting NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory transmission. The compound has undergone early-stage clinical development, including Phase IIa proof-of-concept trials targeting neuropathic pain conditions. These trials explored its safety, tolerability, and efficacy in humans. Results suggested that CNS-5161 hydrochloride can provide analgesic effects by modulating NMDA receptor activity, which is involved in the development and maintenance of chronic pain states. However, as with many NMDA antagonists, clinical use requires careful consideration due to the receptor's important physiological functions. Beyond clinical potential, CNS-5161 hydrochloride is used in research laboratories to study synaptic plasticity and the molecular mechanisms of excitotoxicity. Its ability to selectively block NMDA receptor ion channels without affecting other glutamate receptors has facilitated detailed examination of the receptor's contribution to learning, memory, and neurotoxicity. The chemical compound is supplied as a lyophilized powder, stable under appropriate storage conditions. It can be reconstituted for in vitro and in vivo experiments, allowing researchers to investigate NMDA receptor-mediated pathways and test novel therapeutic approaches for neurological diseases. Applications of CNS-5161 hydrochloride extend to models of epilepsy, ischemic stroke, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. By preventing excessive calcium influx through NMDA receptor channels, CNS-5161 reduces neuronal injury and helps clarify the receptor’s involvement in these pathologies. It also serves as a lead compound in the design of newer NMDA receptor antagonists with improved specificity and reduced side effects. In summary, CNS-5161 hydrochloride is a significant NMDA receptor ion channel antagonist discovered through targeted medicinal chemistry efforts. It is valuable both as a research tool and as a candidate molecule in the development of therapies addressing conditions involving NMDA receptor overactivation. Its demonstrated neuroprotective and analgesic properties underscore the importance of selective NMDA receptor modulation in neuropharmacology and clinical neuroscience. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for CNS-5161 hydrochloride |