Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hubei Innerse Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (027) 8818-9299 | |||
 |
sales@innersebio.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | (4S)-2-(5,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 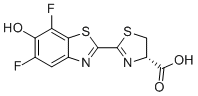 |
| Molecular Formula | C11H6F2N2O3S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 316.30 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1629896-95-2 |
| SMILES | C1[C@@H](N=C(S1)C2=NC3=CC(=C(C(=C3S2)F)O)F)C(=O)O |
|
(4S)-2-(5,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid is a heterocyclic organic compound that combines two sulfur- and nitrogen-containing ring systems within a single, stereochemically defined molecule. Its structure incorporates a benzothiazole moiety substituted with fluorine atoms and a phenolic hydroxyl group, fused through a carbon–carbon linkage to a partially saturated 1,3-thiazole ring bearing a carboxylic acid function. The presence of a defined (4S) stereocenter distinguishes this compound from racemic analogues and is significant in contexts where biological recognition is sensitive to molecular chirality. The emergence of compounds with this general structural pattern is closely associated with developments in medicinal and bioorganic chemistry rather than with classical industrial chemistry. Benzothiazole derivatives have been studied for many decades because the benzothiazole ring system is frequently encountered in biologically active molecules. Substitution with halogen atoms such as fluorine is a well-established strategy in medicinal chemistry, as fluorine can modulate electronic properties, metabolic stability, and binding interactions without substantially increasing steric bulk. Similarly, thiazole and thiazoline derivatives are common motifs in natural products and synthetic bioactive compounds, often contributing to binding affinity toward enzymes or receptors. The specific compound bearing both a benzothiazole and a dihydrothiazole-4-carboxylic acid unit appears in the scientific record as part of systematic explorations of heterocyclic scaffolds for biological activity. Rather than being discovered as a naturally occurring substance, it is understood to be the result of targeted synthetic design. Such compounds are typically prepared through multi-step synthetic routes involving the construction of each heterocyclic ring followed by coupling and stereoselective transformations. The incorporation of the carboxylic acid group provides a polar, ionizable functionality that is frequently exploited to enhance aqueous solubility and to enable specific interactions with biological targets. The interest in this class of molecules is largely driven by their evaluation in medicinal chemistry research. Benzothiazole-containing compounds have been investigated in a variety of therapeutic areas, including antimicrobial, anticancer, and enzyme inhibition studies. The attachment of a thiazoline or thiazole ring bearing a carboxylic acid further expands the range of possible interactions with proteins, particularly through hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions. While the exact biological role of (4S)-2-(5,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid has not been widely reported as a standalone compound, its structure aligns with motifs commonly explored as lead compounds or intermediates in drug discovery programs. In addition to direct biological screening, compounds of this type may serve as reference structures or synthetic intermediates. The presence of both heteroaromatic and partially saturated heterocyclic rings allows chemists to probe structure–activity relationships by systematic modification of substituents such as the fluorine atoms, the hydroxyl group, or the carboxylic acid functionality. The defined stereochemistry at the 4-position of the thiazoline ring is particularly relevant, as enantiomerically pure compounds are often required to accurately assess biological activity and to minimize off-target effects. From an application standpoint, the compound is best understood as a research chemical rather than a bulk or commercial product. Its primary use lies in laboratory-scale studies focused on understanding how complex heterocyclic frameworks interact with biological systems. Such investigations contribute to the broader knowledge base of medicinal chemistry by identifying structural features that enhance potency, selectivity, or pharmacokinetic behavior. Even when a specific compound does not advance to clinical development, the data obtained from its study can inform the design of subsequent generations of molecules. Overall, (4S)-2-(5,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid represents a deliberately designed heterocyclic molecule situated within the well-established traditions of benzothiazole and thiazole chemistry. Its discovery reflects targeted synthetic efforts in medicinal chemistry, and its applications are centered on exploratory research aimed at understanding and exploiting the biological potential of complex, fluorinated heterocyclic scaffolds. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (4S)-2-(5,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid |