Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Zhangjiagang Pharmabl Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (512) 5818-9390 | |||
 |
info@pharmabl.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| SL Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd. | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (40) 6661-1133 | |||
 |
enquiry@sldrugs.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 1999 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| SRC Laboratories Pvt Ltd | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (40) 2307-7999 | |||
 |
info@srclaboratories.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Intatrade Chemicals GmbH | Germany | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+49 (3493) 605-465 | |||
 |
sales@intatrade.de | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Amadis Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8992-5085 | |||
 |
sales@amadischem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2010 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Aromatic aldehyde (containing acetal, hemiacetal) |
|---|---|
| Name | 5-Bromosalicylaldehyde |
| Synonyms | 5-Bromo-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde |
| Molecular Structure | 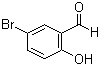 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5BrO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 201.02 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1761-61-1 |
| EC Number | 217-167-2 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1Br)C=O)O |
| Melting point | 103-107 ºC |
|---|---|
| Water solubility | insoluble |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5-Bromosalicylaldehyde is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H5BrO2. It consists of a salicylaldehyde structure, with a bromine atom positioned at the 5-position of the benzene ring. The compound is synthesized by introducing a bromine atom to the aromatic ring of salicylaldehyde. Typically, this reaction is carried out through electrophilic aromatic substitution, where bromine is added in the presence of a catalyst, often iron or aluminum bromide. The first known synthesis of 5-bromosalicylaldehyde can be traced back to early studies in organic chemistry, where researchers were focused on modifying the salicylaldehyde molecule to create compounds with different chemical reactivity and properties. This compound, due to its bromine substitution, exhibits altered physical and chemical characteristics compared to its parent compound, salicylaldehyde. 5-Bromosalicylaldehyde finds utility primarily in organic synthesis and as an intermediate in the production of various chemical derivatives. Its reactivity is enhanced by the electron-withdrawing effect of the bromine atom at the 5-position of the aromatic ring, making it a useful building block for the synthesis of more complex molecules. For instance, 5-bromosalicylaldehyde can be employed in the preparation of metal complexes, especially those involving coordination with metals such as copper and iron. These complexes often have applications in catalysis and material science. The compound also plays a role in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates. Salicylaldehyde derivatives are of interest due to their biological activity, particularly in the development of anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial agents. The introduction of a bromine atom into the salicylaldehyde molecule can modulate its biological activity, making 5-bromosalicylaldehyde an important intermediate in medicinal chemistry. In addition to pharmaceutical applications, 5-bromosalicylaldehyde is used in the synthesis of various functionalized aromatic compounds. The bromine atom on the aromatic ring makes it a good candidate for nucleophilic substitution reactions, where it can react with nucleophiles such as amines, alcohols, or thiols. This versatility in reactivity contributes to its importance in synthetic chemistry, particularly in the creation of custom molecules with specific properties. The compound is also of interest in the development of fluorescent materials. 5-Bromosalicylaldehyde can be used as a precursor in the synthesis of fluorescent dyes and sensors, which are valuable in analytical chemistry for detecting specific ions or molecules. These applications benefit from the electronic properties introduced by the bromine atom and the aldehyde group, which can be further manipulated to enhance the fluorescence of the resulting materials. In conclusion, 5-bromosalicylaldehyde is a versatile and valuable compound in synthetic organic chemistry. Its primary applications are in the synthesis of metal complexes, pharmaceutical intermediates, functionalized aromatic compounds, and fluorescent materials. Its discovery and use are well-documented in the literature, and its properties make it a useful reagent in various fields of chemistry. References 1979. New dioxouranium(VI) complexes with tridentate dibasic Schiff bases containing ONO donor sets. Transition Metal Chemistry, 4(3). DOI: 10.1007/bf00619063 2023. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Anticancer Studies of Cubane-Type Ni(II) Complex Derived from 5-bromosalicylaldehyde-2-aminophenol Schiff Base. Journal of Cluster Science, 34(6). DOI: 10.1007/s10876-023-02457-0 2024. Synthesis, Antimicrobial, and DNA-Binding Evaluation of Novel Schiff Bases Containing Tetrazole Moiety And Their Ni(II) and Pt(II) Complexes. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 57(10). DOI: 10.1007/s11094-024-03056-7 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 5-Bromosalicylaldehyde |