Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| MolScanner | Singapore | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18621675448 | |||
 |
marketing@molscanner.com | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 9896 7603 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2025 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Salt of carboxylic acid ester and its derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | 4,6-Dichloro-pyridazine-3-carboxylic acid lithium salt monohydrate |
| Molecular Structure | 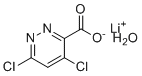 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H3Cl2LiN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 216.94 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2245111-15-1 |
| EC Number | 878-344-3 |
| SMILES | [Li+].C1=C(C(=NN=C1Cl)C(=O)[O-])Cl.O |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
4,6-Dichloro-pyridazine-3-carboxylic acid lithium salt monohydrate is a synthetic organolithium compound derived from pyridazine, a six-membered aromatic heterocycle containing two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 2. This compound consists of a dichlorinated pyridazine ring with chlorine atoms at the 4- and 6-positions, a carboxylic acid function at the 3-position, neutralized with lithium cation to form a lithium carboxylate, and one molecule of water of hydration. The discovery and preparation of substituted pyridazine derivatives, including 4,6-dichloropyridazine-3-carboxylic acid and its salts, trace back to mid-20th-century heterocyclic chemistry research. The introduction of electron-withdrawing chlorine atoms on the aromatic ring system increases the chemical reactivity of the pyridazine nucleus, particularly toward nucleophilic substitution. The lithium salt form is generally obtained by treating the corresponding free acid with lithium hydroxide in aqueous or alcoholic media, followed by crystallization in the presence of water to yield the monohydrate. This lithium salt is primarily used as an intermediate in pharmaceutical and agrochemical research, especially for the synthesis of biologically active compounds. The presence of two chlorine atoms on the ring permits selective substitution with nucleophiles such as amines or alkoxides, allowing the preparation of a broad range of substituted pyridazines with potential pharmacological properties. Its carboxylic acid moiety, converted into various esters or amides, is often a key point of derivatization in structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies. One notable area of application involves the development of herbicides and plant growth regulators. Pyridazine derivatives have been reported to inhibit specific enzymatic processes in plant metabolism, and the dichloropyridazine scaffold has served as a core structure in the discovery of compounds affecting photosynthesis or cell division in target species. The lithium salt form facilitates handling and solubility in various reaction media, making it a preferred starting material for laboratory-scale synthesis. In medicinal chemistry, pyridazine-based frameworks are investigated for a range of bioactivities including anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antiviral, and antimicrobial properties. The dichloro-substitution pattern allows for controlled functionalization that is critical for optimizing biological target selectivity and improving pharmacokinetic profiles. Derivatives synthesized from 4,6-dichloro-pyridazine-3-carboxylic acid lithium salt have also been evaluated for kinase inhibition and receptor modulation in central nervous system disorders. The monohydrate nature of the compound indicates the presence of a single water molecule per formula unit in the crystal lattice. This can impact both the physical properties (such as hygroscopicity and crystallinity) and the reactivity of the material. Controlled drying and storage conditions are typically required to preserve the compound's integrity and prevent the loss of water of hydration, which may lead to changes in its solubility and handling characteristics. Overall, 4,6-dichloro-pyridazine-3-carboxylic acid lithium salt monohydrate represents a versatile intermediate useful in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds with diverse chemical and biological profiles. Its reactivity and functional groups enable the generation of libraries of analogs that are essential for modern drug and agrochemical discovery programs. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 4,6-Dichloro-pyridazine-3-carboxylic acid lithium salt monohydrate |