Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| MolScanner | Singapore | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18621675448 | |||
 |
marketing@molscanner.com | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 9896 7603 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2025 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Isoquinoline compound |
|---|---|
| Name | 8-Chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine |
| Molecular Structure | 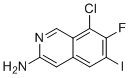 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H5ClFIN2 |
| Molecular Weight | 322.51 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2246363-09-5 |
| SMILES | C1=C2C=C(N=CC2=C(C(=C1I)F)Cl)N |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 442.3±40.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 221.3±27.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.752 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P501-P270-P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313-P301+P312+P330 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
8-Chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine is a chemical compound that contains a substituted isoquinoline structure with three halogen atoms—chlorine (Cl), fluorine (F), and iodine (I)—attached at specific positions on the aromatic ring, along with an amine group (-NH2) at the 3-position of the isoquinoline. The specific arrangement of these substituents influences both the chemical reactivity and the potential biological activity of the compound. Isoquinolines, like this one, are an important class of organic compounds that are widely studied for their biological activity. The presence of halogens on the isoquinoline ring significantly modifies the compound's properties. Chlorine, fluorine, and iodine are electron-withdrawing groups, and their positions on the ring affect the compound's electronic distribution and reactivity. This can influence the compound's ability to interact with other molecules, such as enzymes, receptors, and other cellular targets. The amine group (-NH2) attached to the isoquinoline ring further enhances the compound's reactivity, particularly in nucleophilic substitution reactions. The amine group also enables the compound to form bonds with biological macromolecules, which may be relevant for medicinal or pharmaceutical applications. The synthesis of 8-chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine typically involves halogenation reactions to selectively introduce the chlorine, fluorine, and iodine substituents at the appropriate positions on the isoquinoline ring, followed by an amination step to introduce the amine group at position 3 of the ring. This can be achieved through a variety of synthetic methods, including electrophilic aromatic substitution for halogenation and nucleophilic substitution for introducing the amine group. As for its applications, 8-chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine may be of interest in the field of medicinal chemistry, where isoquinoline derivatives are known for a range of biological activities, including antimicrobial, anticancer, and neuroactive properties. The combination of halogens and the amine group could enhance the compound's biological potency, selectivity, and stability. Additionally, the halogenated isoquinoline structure might be used as a scaffold for the development of more complex therapeutic agents or as a molecular probe for studying biological processes. In the field of materials science, the compound could be explored for its potential applications in designing novel materials or molecular electronics, where the unique properties imparted by the halogen atoms could influence the compound’s interaction with other substances, such as in the creation of conductive or optoelectronic materials. Overall, 8-chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine is a potentially versatile compound with applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science, driven by its unique structure and the influence of the halogenated substituents on its reactivity and biological activity. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 8-Chloro-7-fluoro-6-iodoisoquinolin-3-amine |