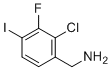
(2-Chloro-3-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)methanamine is an organic compound consisting of a phenyl ring with three halogen substituents (chlorine, fluorine, and iodine) at specific positions, along with a methanamine group (-CH2NH2) attached to the benzene ring. The structure and substituent positioning contribute to its potential reactivity, making it an interesting compound for various applications in medicinal chemistry, material science, and chemical synthesis.
The presence of halogens—chlorine, fluorine, and iodine—on the phenyl ring influences the compound's electronic properties. Each halogen exhibits electron-withdrawing effects that modify the reactivity of the aromatic ring, particularly in electrophilic substitution reactions, and can also affect the compound's biological activity. The methanamine group provides an additional functional site, which may contribute to interactions with biological molecules such as proteins, enzymes, or receptors.
The synthesis of (2-chloro-3-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)methanamine generally involves halogenation of a suitable precursor, followed by introduction of the amine group at the desired position on the aromatic ring. Techniques such as nucleophilic aromatic substitution or electrophilic aromatic substitution are commonly used for introducing halogen substituents, while the amine group can be added through a variety of synthetic pathways.
In terms of applications, (2-chloro-3-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)methanamine may be of interest in medicinal chemistry, particularly as a building block for the synthesis of biologically active compounds. The combination of the amine group and halogenated phenyl ring can impart unique properties, potentially contributing to the development of molecules with antimicrobial, anticancer, or other therapeutic activities. The structural modifications introduced by the halogens can also provide increased selectivity and potency in drug design.
Additionally, the compound's unique substituent pattern could be useful in materials science, such as in the design of specialized polymers or other functional materials. The halogens can influence the solubility, stability, and electronic properties of materials, which may make compounds like (2-chloro-3-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)methanamine valuable for various industrial applications.
Overall, (2-chloro-3-fluoro-4-iodophenyl)methanamine is a versatile compound with potential applications in pharmaceutical development, chemical synthesis, and materials science, driven by the influence of its halogenated aromatic structure and the reactive amine group. Its ability to undergo a variety of chemical reactions makes it a useful intermediate in the creation of more complex molecules with specific properties tailored to various fields of research.
|



 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details