Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Chengxi Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 18916572267 | |||
 |
chengxitechco@163.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: +8618916572267 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Heterocyclic compound >> Pyrroles |
|---|---|
| Name | 1H-Pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde |
| Molecular Structure | 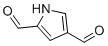 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H5NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 123.11 |
| CAS Registry Number | 23999-91-9 |
| SMILES | C1=C(NC=C1C=O)C=O |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3, Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Index of Refraction | 1.674, Calc.* |
| Boiling Point | 312.9±27.0 ºC (760 mmHg), Calc.* |
| Flash Point | 147.5±30.1 ºC, Calc.* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
1H-Pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde is a bifunctional heterocyclic compound featuring a pyrrole ring substituted with aldehyde groups at the 2- and 4-positions. As a derivative of pyrrole, a five-membered aromatic heterocycle containing a nitrogen atom, it falls within a broad class of nitrogen-containing compounds that have received sustained attention in both organic synthesis and coordination chemistry. The synthesis and structural characterization of 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde were first explored in the context of functionalized heterocycles designed for extended conjugation and as intermediates in the construction of more complex organic molecules. The selective introduction of formyl groups at the 2- and 4-positions of the pyrrole ring is commonly achieved through formylation reactions such as the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction, starting from unsubstituted or protected pyrroles under controlled electrophilic conditions. The utility of 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde in synthetic chemistry is primarily due to the electrophilic reactivity of its aldehyde groups and the electron-rich character of the pyrrole core. This compound is frequently employed as a precursor in the construction of conjugated organic frameworks, particularly in the synthesis of porphyrins and related macrocyclic structures. These macrocycles are often prepared by condensation reactions involving 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde and other aldehydes or ketones in the presence of acid catalysts, leading to tetrapyrrolic compounds of interest in materials chemistry, photodynamic therapy, and catalysis. One significant application of 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde is in the synthesis of linear and cyclic oligopyrroles, which serve as ligands for metal complexation or as components of supramolecular assemblies. In these roles, the aldehyde groups provide anchor points for cross-linking or further derivatization with amines or hydrazides to form imines, hydrazones, or Schiff bases. Such derivatives have been investigated for use in chemosensors, fluorescent probes, and electroactive materials. The compound has also been studied for its role in generating donor–acceptor systems when incorporated into π-conjugated architectures. In molecular electronics and organic photovoltaics, it may be employed as a building block for constructing electron-donating frameworks that can be tuned for desired optoelectronic properties through systematic modification of its substituents or surrounding molecular environment. In coordination chemistry, 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde has been utilized in the synthesis of polydentate ligands. Upon condensation with primary amines or diamines, it can form Schiff base ligands that coordinate with various transition metals, resulting in metal complexes with defined geometric and electronic properties. These complexes are studied for catalytic activity in oxidation, hydrogenation, and cross-coupling reactions, as well as for their magnetic or luminescent behavior. Additionally, the compound serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of functional dyes and pigments. The presence of two aldehyde functionalities enables the formation of chromophores with extended conjugation, particularly in the development of fluorescent materials for imaging or sensing applications. Due to the reactivity of the aldehyde groups, 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde must be handled under appropriate conditions to avoid undesired polymerization or degradation. It is generally stored under an inert atmosphere and used in anhydrous solvents to maintain stability and reactivity in synthetic applications. The significance of 1H-pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde lies in its role as a versatile bifunctional precursor for the assembly of a wide range of complex organic and organometallic systems. Its established applications span the fields of materials science, catalysis, supramolecular chemistry, and biomedical research, making it a valuable component in modern chemical synthesis. References 2015. A facile synthesis of diformylated pyrroles by dehydroxylation of N-aryl-5-hydroxy-gamma-lactam derivatives under Vilsmeier reaction conditions. Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, 51(10). DOI: 10.1007/s10593-015-1789-z |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1H-Pyrrole-2,4-dicarbaldehyde |