Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Rui Yun Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 6726-7633 | |||
 |
sales@rychemical.com.cn | |||
 |
WeChat: 13917251563 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Aromatic aldehyde (containing acetal, hemiacetal) |
|---|---|
| Name | 2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde |
| Molecular Structure | 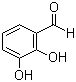 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 138.12 |
| CAS Registry Number | 24677-78-9 |
| EC Number | 246-398-1 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C(=C1)O)O)C=O |
| Melting point | 104-109 ºC |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde, also known as o-dihydroxybenzaldehyde, is an aromatic compound featuring both aldehyde and hydroxyl functional groups. Its chemical formula is C₇H₆O₄, and it is structurally characterized by a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups positioned ortho to each other and an aldehyde group. The presence of these functional groups imparts unique chemical properties to 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde, making it an important compound in organic chemistry. The discovery of 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde dates back to the late 19th century when chemists were exploring the reactivity and properties of substituted benzaldehydes. The compound was initially identified through various chemical reactions involving ortho-dihydroxybenzenes and related aldehydes. Researchers observed that the combination of hydroxyl and aldehyde groups in the ortho position resulted in distinct reactivity patterns, which were of significant interest for further study. In organic synthesis, 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde serves as a versatile intermediate for the preparation of various derivatives and complex molecules. Its ability to participate in diverse chemical reactions, such as oxidation and condensation, makes it valuable in the synthesis of compounds used in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. For instance, it can be used to synthesize flavonoid derivatives and other bioactive molecules. The compound also plays a role in medicinal chemistry due to its biological activity. Research has shown that 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and its derivatives exhibit antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. These biological activities are attributed to the presence of the hydroxyl groups, which enhance the compound’s ability to scavenge free radicals and interact with biological targets. As a result, 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde has been investigated for potential applications in the development of therapeutic agents and health supplements. In addition to its applications in medicine, 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde is utilized in various industrial processes. It is employed as a reagent in chemical analysis and as a precursor in the manufacture of dyes and pigments. The compound’s reactivity and ability to form complex structures make it suitable for these applications, contributing to its importance in both research and industry. Overall, 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde is a significant compound in organic chemistry, with applications spanning from synthesis and medicine to industrial processes. Its unique combination of functional groups and reactivity continues to make it a subject of interest for ongoing research and development. References 2024. A novel chemical route for low-temperature curing of natural rubber using 2,4 dihydroxybenzaldehyde: improved thermal and tensile properties. *Iranian Polymer Journal*, 33(5). DOI: 10.1007/s13726-024-01297-7 2023. Synergistic effects of 2,4 dihydroxybenzaldehyde and carbon black nanoparticles on the properties of natural rubber. *Emergent Materials*, 6(3). DOI: 10.1007/s42247-023-00528-6 2023. Sandwich-like construction of a new aminated chitosan Schiff base for efficient removal of Congo red. *Applied Water Science*, 13(2). DOI: 10.1007/s13201-023-01866-w |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2,3-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde |