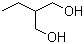
2-Ethylpropane-1,3-diol is an organic compound belonging to the class of diols, which are characterized by the presence of two hydroxyl groups (-OH) attached to different carbon atoms within a three-carbon chain. The structure of 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol consists of an ethyl group (C2H5) attached to the second carbon of a propane-1,3-diol backbone, giving it both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties. These properties make 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol an attractive building block for various applications in the chemical, polymer, and material industries.
The discovery of 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol emerged as part of the broader research into functionalized diols with the aim of creating new intermediates that could enhance the properties of polymers, coatings, and other industrial chemicals. The compound's structure allows it to bridge the gap between hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments, making it an ideal candidate for use in materials where both water resistance and stability are required.
Synthesis of 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol typically involves the reaction of ethylene oxide with ethanol or other ethyl-based reagents, often under controlled conditions using a suitable catalyst. This method allows for efficient production of the diol, which can then be utilized in various industrial processes. The synthesis of 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol is straightforward, and the compound is produced on a large scale for use in different chemical applications.
One of the primary uses of 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol is in the production of polyesters and polyurethanes. As a monomer, it imparts flexibility, hydrophobicity, and improved processing characteristics to these materials. In polyesters, 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol helps to improve the overall mechanical properties and water resistance of the final polymer. Similarly, in polyurethanes, it enhances the flexibility and durability of the polymer, making it useful in coatings, adhesives, sealants, and other applications that require long-lasting, high-performance materials.
2-Ethylpropane-1,3-diol also finds application in the formulation of surfactants and emulsifiers. The combination of the ethyl group and hydroxyl groups provides a balance of solubility, allowing the compound to be used as a stabilizer in emulsions. This makes it useful in the production of cleaning agents, detergents, and other industrial formulations where both oil and water compatibility are needed. The compound's mild reactivity also makes it useful in the synthesis of other chemicals, such as plasticizers, that are essential in the production of flexible plastics and synthetic rubbers.
Additionally, 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol has been explored for use in the cosmetics and personal care industries. Its mild nature, low toxicity, and ability to act as a humectant make it a valuable ingredient in skin care products, such as moisturizers and lotions. By retaining moisture in the skin, it can help improve the texture and hydration properties of cosmetic formulations, making it an attractive candidate for further investigation in this field.
As industries move towards more sustainable and eco-friendly products, the importance of versatile compounds like 2-ethylpropane-1,3-diol will continue to grow. Its ability to enhance the properties of materials, combined with its potential for use in a variety of applications, makes it a valuable building block for the development of new, high-performance products.
|
















 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details