Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Ningbo Dongbo New Energy Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0574) 6329-6893 | |||
 |
alice@dobonewenergy.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 18668281331 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 15824288686 | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2020 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Catalysts and additives >> Polymer |
|---|---|
| Name | 2-methyl-2-Propenoic acid methyl ester polymer with butyl 2-propenoate and 2-propenoic acid |
| Synonyms | Methyl methacrylate butyl acrylate acrylic acid polymer |
| Molecular Structure | 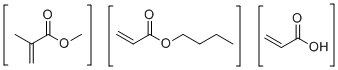 |
| Molecular Formula | (C7H12O2)x.(C5H8O2)x.(C3H4O2)x |
| CAS Registry Number | 26300-51-6 |
| EC Number | 607-906-0 |
| SMILES | C=C(C(OC)=O)C.C=CC(=O)OCCCC.C=CC(=O)O |
|
The polymer formed from 2-methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl ester, butyl 2-propenoate, and 2-propenoic acid is a copolymer consisting of methyl methacrylate, butyl acrylate, and acrylic acid monomer units. This terpolymer is synthesized via free radical polymerization or controlled radical polymerization methods, allowing for control over composition, molecular weight, and polymer architecture. The combination of these monomers results in a polymer with tailored mechanical, chemical, and physical properties suited for various applications. Methyl methacrylate (2-methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl ester) contributes rigidity, hardness, and optical clarity to the copolymer due to its bulky methyl side group and ester functionality. Butyl acrylate (butyl 2-propenoate) imparts flexibility and impact resistance by introducing longer, more flexible alkyl side chains. Acrylic acid (2-propenoic acid) introduces carboxylic acid functional groups that increase hydrophilicity and provide sites for further chemical modification or crosslinking. The polymerization typically involves mixing the three monomers in specific ratios, followed by initiation using thermal or photochemical radical initiators. Reaction conditions such as temperature, solvent, and initiator concentration influence the molecular weight and distribution, while copolymer composition dictates the balance between hardness, flexibility, and chemical reactivity. Advanced polymerization techniques such as atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization enable precise control of polymer structure and functionality. This terpolymer finds extensive use in coatings, adhesives, and sealants due to its balanced properties. The presence of methyl methacrylate units ensures good hardness and weather resistance, while butyl acrylate units improve flexibility, reducing brittleness in the final product. Acrylic acid units enhance adhesion to various substrates and enable crosslinking reactions, improving durability and chemical resistance. Such copolymers are commonly formulated for architectural paints, automotive coatings, and pressure-sensitive adhesives. In addition to coatings, this polymer is utilized in textile finishes, paper coatings, and as a binder in various composite materials. Its water dispersibility and film-forming ability facilitate its use in waterborne formulations, which align with environmental regulations aiming to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. The polymer’s adjustable glass transition temperature and mechanical properties can be tuned by varying monomer ratios, enabling customization for specific end-use requirements. Biomedical applications have also been explored due to the biocompatibility of the acrylic acid moieties and the ability to modify polymer surfaces for drug delivery or tissue engineering scaffolds. The presence of carboxyl groups allows for conjugation with bioactive molecules and enhances hydrophilicity, which is important for biological interactions. Environmental considerations focus on the polymer’s stability, non-biodegradability, and recyclability. While generally resistant to environmental degradation, research into copolymer blends and the incorporation of biodegradable monomers seeks to improve sustainability. The use of waterborne formulations further reduces environmental impact by minimizing solvent emissions during processing. Overall, the polymer formed from 2-methyl-2-propenoic acid methyl ester, butyl 2-propenoate, and 2-propenoic acid represents a versatile material with a balance of hardness, flexibility, and chemical functionality. Its widespread use in coatings, adhesives, and biomedical applications demonstrates its importance in modern polymer science and industrial practice. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 2-methyl-2-Propenoic acid methyl ester polymer with butyl 2-propenoate and 2-propenoic acid |