Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Tianjin Zhongxin Chem-tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (22) 6688-0623 | |||
 |
sales@tjzxchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2009 | ||||
| Classification | Catalysts and additives >> Polymer |
|---|---|
| Name | 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene |
| Synonyms | Polyisocyanate based on TDI and HDI |
| Molecular Structure | 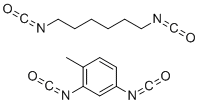 |
| Molecular Formula | C17H18N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 342.35 |
| CAS Registry Number | 26426-91-5 |
| EC Number | 927-271-6 |
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)N=C=O)N=C=O.C(CCCN=C=O)CCN=C=O |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H317-H319 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264+P265-P272-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P321-P333+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
|
1,6-Diisocyanatohexane 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene is a combination of two important diisocyanates: 1,6-diisocyanatohexane, an aliphatic compound, and 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene, commonly known as toluene diisocyanate (TDI), an aromatic compound. These diisocyanates are widely used in the production of polyurethanes, which are versatile materials applied in a variety of industries. Their discovery and development significantly advanced polyurethane chemistry, providing materials with enhanced mechanical properties, flexibility, and durability. 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane, also referred to as hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI), was first synthesized as part of the development of aliphatic isocyanates in the mid-20th century. It is known for its role in producing polyurethanes with improved weather and light stability, making it suitable for outdoor applications. TDI, an aromatic diisocyanate, was discovered earlier and gained widespread industrial use due to its ability to create strong, rigid polyurethanes. Together, these two compounds offer a balance of properties that cater to both flexibility and toughness, making them essential components in various polyurethane formulations. Polyurethanes made from 1,6-diisocyanatohexane and 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene have diverse applications, most notably in the manufacture of foams, coatings, elastomers, and adhesives. Polyurethane foams, which are classified into flexible and rigid types, are widely used in furniture, automotive seats, insulation, and packaging. Flexible foams offer cushioning and comfort, while rigid foams provide excellent thermal insulation for use in refrigeration and construction. The inclusion of 1,6-diisocyanatohexane in the formulation helps enhance the foam's stability in outdoor environments, while TDI provides structural integrity. Polyurethane coatings derived from these diisocyanates offer excellent protective qualities, such as resistance to UV radiation, abrasion, and chemicals. These coatings are applied in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries, where materials are exposed to harsh environmental conditions. The combination of aliphatic and aromatic diisocyanates results in coatings that are both durable and flexible, ensuring long-term protection of surfaces while maintaining their appearance. This makes them especially valuable for automotive finishes and protective coatings on machinery and infrastructure. In the field of adhesives and sealants, polyurethanes based on 1,6-diisocyanatohexane and TDI provide strong bonding capabilities, particularly in applications that require durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture. These adhesives are widely used in construction, electronics, and transportation. Their rapid curing properties and high adhesive strength make them suitable for demanding industrial environments where robust bonding is essential. Polyurethane elastomers made from these diisocyanates exhibit a combination of toughness and elasticity, making them ideal for applications such as wheels, gaskets, seals, and other industrial components. Their ability to withstand wear, chemicals, and environmental stress allows for their use in critical applications that require both flexibility and mechanical strength. Despite their widespread use, diisocyanates, including 1,6-diisocyanatohexane and 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene, pose health risks, particularly through inhalation or skin contact. Exposure to these compounds can lead to respiratory issues, including asthma, making it necessary to handle them with care. Industries that use diisocyanates have implemented strict safety measures, such as proper ventilation, protective equipment, and exposure monitoring to mitigate health risks to workers. The use of 1,6-diisocyanatohexane 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene in polyurethane chemistry continues to be vital for producing materials with specific mechanical properties and environmental resilience. Their applications in foams, coatings, elastomers, and adhesives demonstrate the versatility of these diisocyanates in modern industrial and consumer products. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1,6-Diisocyanatohexane 2,4-diisocyanato-1-methylbenzene |