Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Sulfonate / sulfinate |
|---|---|
| Name | Bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide |
| Synonyms | SPS |
| Molecular Structure | 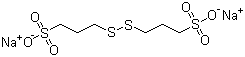 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12Na2O6S4 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.40 |
| CAS Registry Number | 27206-35-5 |
| EC Number | 248-324-3 |
| SMILES | C(CSSCCCS(=O)(=O)[O-])CS(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+] |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H317 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P272-P280-P302+P352-P321-P333+P317-P362+P364-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide is a sulfur-containing compound characterized by two sulfopropyl groups connected by a disulfide bond. Its discovery was driven by the need for compounds with sulfur linkages that could act as additives and stabilizers in various chemical processes. The presence of the disulfide bond and sulfonate groups gives this compound unique properties, making it useful in applications ranging from electroplating to polymer modification. The synthesis of bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide typically involves the reaction of sodium 3-mercaptopropanesulfonate, where two of these molecules form a disulfide linkage under oxidative conditions. This creates a stable disulfide bond while maintaining the sulfonate groups, which provide water solubility and ionic character. This solubility in aqueous environments allows the compound to be utilized in various industrial processes that require water-based systems. One of the major applications of bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide is in electroplating, particularly in the deposition of metals such as copper and nickel. The compound is used as an additive to improve the quality and uniformity of metal coatings, enhancing the brightness, smoothness, and overall consistency of the plated surface. In the electronics industry, the compound plays a crucial role in ensuring the production of high-quality circuit boards by improving the adhesion and structure of metal layers during the plating process. In addition to its role in electroplating, bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide has been explored in polymer chemistry. It is used as a crosslinking agent to introduce disulfide bonds into polymer chains, enhancing the material's stability and elasticity. This modification is particularly valuable in the development of elastomers, coatings, and adhesives, where the disulfide bonds provide increased durability and resistance to environmental degradation. The compound's sulfonate groups also contribute to its role in water treatment processes. It can act as a stabilizer for metal ions in solution, preventing unwanted precipitation and ensuring that the metal ions remain available for reactions. This stabilizing effect has been leveraged in various industrial applications, including wastewater treatment, where bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide helps control the behavior of metal contaminants. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bis-(sodium sulfopropyl)-disulfide |