Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Zhejiang Bw Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13868966491 | |||
 |
sales@peekmaterials.com | |||
 |
WeChat: ZHEJIANG BW INDUSTRY CO., LTD | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2008 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Hubei Marvel-bio Medicine Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (027) 8773-8507 | |||
 |
maoerwo123@163.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: kangbao813 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Catalysts and additives >> Polymer |
|---|---|
| Name | Poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) |
| Molecular Structure | 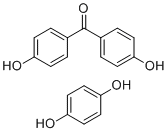 |
| Molecular Formula | (OC6H4OC6H4COC6H4)n |
| CAS Registry Number | 29658-26-2 |
| EC Number | 608-392-0 |
| SMILES | Oc1ccc(O)cc1.Oc2ccc(cc2)C(=O)c3ccc(O)cc3 |
| Density | 1.3 g/mL (25 ºC) (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 322 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | all common solvents: insoluble, concentrated sulfuric acid: soluble (Expl.) |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P280-P302+P352-P337+P313-P305+P351+P338-P362+P364-P332+P313 Details |
|
Poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) is a high-performance aromatic polyester known for its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. It belongs to the class of polymers characterized by repeating aromatic units connected through ester and ether linkages, which contribute to its rigidity and high glass transition temperature. The polymer is a member of the polyarylate family, a group of materials valued for their stability under extreme thermal and oxidative conditions. The development of this polymer is rooted in the mid-20th century research on aromatic polyesters. Initial studies focused on creating polymers that combined the structural rigidity of aromatic rings with the functional versatility of ester and ether linkages. The synthesis typically involves the polycondensation of dihydroxy aromatic compounds with aromatic dicarboxylic acid derivatives, producing high-molecular-weight polymers with repeating units containing alternating ether and ester groups. This method allows precise control over polymer chain length and molecular weight, which in turn affects mechanical properties and processability. Poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) finds applications in areas requiring materials with excellent thermal and chemical resistance. Its high thermal stability makes it suitable for components in electronics and electrical engineering, such as insulating films, circuit boards, and connectors. The polymer’s chemical resistance also allows its use in chemical processing equipment, where exposure to acids, bases, and organic solvents is common. In addition, its dimensional stability and rigidity are advantageous in optical devices and high-precision mechanical components. The polymer’s aromatic backbone provides exceptional mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and modulus, which are retained even at elevated temperatures. This performance makes it suitable for advanced engineering applications where conventional polymers would deform or degrade. Moreover, the presence of ether linkages enhances flexibility compared with fully aromatic polyesters, enabling easier processing into films, fibers, or molded components. Its inherent flame resistance further expands its use in aerospace, automotive, and electronic applications. In terms of chemical reactivity, the polymer is largely inert due to the stability of its aromatic rings and the strong covalent bonds in the backbone. However, surface modification or functionalization can be performed to improve adhesion, compatibility with other materials, or to introduce specific functionalities such as hydrophilicity or reactive sites for further polymer crosslinking. Such modifications are commonly employed in coatings, composites, and specialized membranes. Processing of poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) typically involves melt extrusion, solution casting, or compression molding. The polymer’s high glass transition temperature requires careful thermal management during processing to prevent degradation, yet its ability to form stable films and molded parts with precise dimensions is highly valued in industrial applications. Additionally, it can be combined with reinforcing agents such as glass fibers or nanoparticles to produce composites with enhanced strength, thermal conductivity, or other targeted properties. Overall, poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) is a versatile aromatic polyester with superior thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. Its use spans electronics, aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries, making it an essential material for applications demanding high-performance polymers that retain stability under extreme conditions. References Najeeb S, Zafar MS, Khurshid Z, Siddiqui F (2016) Applications of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in oral implantology and prosthodontics.J Prosthodont Res 60(1):12–19 DOI: 10.1016/j.jpor.2015.10.001 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Poly(oxy-1,4-phenyleneoxy-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl-1,4-phenylene) |