2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride (commonly known as AIBA) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C8H18Cl2N4. It is a water-soluble azo compound that contains the azo group (-N=N-) and is widely used as a radical initiator in various polymerization processes. AIBA is used in the preparation of polymers and copolymers, and its primary function is to generate free radicals under specific conditions, which initiate the polymerization of unsaturated monomers.
The discovery of AIBA can be traced back to research focused on azo-based radical initiators, specifically those that could be used in aqueous systems. The development of AIBA was driven by the need for initiators that could work in polar solvents and provide controlled polymerization reactions. The addition of the amidine group in AIBA enhances its solubility and reactivity compared to other similar compounds, such as azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN). This modification allows for a broader range of applications, especially in polymerization systems that require water solubility.
AIBA is primarily used in the production of various polymers, including those that are based on acrylate and methacrylate monomers. The compound serves as a free-radical initiator in both bulk and solution polymerization, where it generates radicals upon thermal decomposition. This ability to initiate polymerization makes AIBA an essential component in the preparation of synthetic materials for applications in industries such as plastics, coatings, adhesives, and textiles.
One of the notable applications of AIBA is in controlled or "living" polymerization techniques. In these systems, AIBA can be used to initiate polymerization reactions that allow for precise control over the polymer's molecular weight, structure, and composition. This capability is crucial for the development of high-performance polymers with tailored properties, which are necessary in fields such as nanotechnology, drug delivery, and biomedical engineering.
AIBA has also been employed in the preparation of hydrogels and other advanced materials. The compound's ability to polymerize hydrophilic monomers makes it valuable in the production of hydrogels, which are used in applications ranging from medical devices to water purification. Additionally, AIBA is utilized in the synthesis of copolymers with specific functional properties, such as responsive materials that change shape or characteristics in response to environmental stimuli, like temperature, pH, or ionic strength.
In summary, 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride is a versatile azo compound that plays an important role as a radical initiator in polymer chemistry. Its ability to generate free radicals in aqueous systems makes it an essential component in the synthesis of a wide range of polymers and copolymers. The compound's use in controlled polymerization processes and the creation of advanced materials underscores its significance in modern polymer science and industrial applications.
References
2019. Structural changes of 2,2'-azobis(2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) treated shrimp tropomyosin decrease allergenicity. Food Chemistry, 274.
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.030
2014. In Vitro Susceptibility of Wistar Rat Platelets to Hydrogen Peroxide and AAPH-Induced Oxidative Stress. Indian journal of hematology & blood transfusion : an official journal of Indian Society of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, 30(4).
DOI: 10.1007/s12288-014-0386-0
2009. Optimization and validation of an alternative method to evaluate total reactive antioxidant potential. Analytical Biochemistry, 385(2).
DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2008.10.036
|

















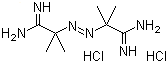


 GHS02;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details