Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Huaian Depon Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (517) 8233-2538 | |||
 |
sales@deponchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Huangshi Bioche Pharmeutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (714) 328-4559 | |||
 |
info@hbbioche.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2018 | ||||
| Volant Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19157790159 13456731436 | |||
 |
sales@volantgroup.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Nanjing Hike Biological Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 5211-0956 | |||
 |
sophia@njhkchem.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 17372769668 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: 17372769668 | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2021 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2024 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Ester >> Methyl ester compound |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl 4-chlorobutyrate |
| Molecular Structure | 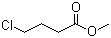 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H9ClO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 136.58 |
| CAS Registry Number | 3153-37-5 |
| EC Number | 221-592-9 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)CCCCl |
| Density | 1.12 |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 175-176 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.4311-1.4331 |
| Flash point | 59 ºC |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS02;GHS07 Warning Details
GHS02;GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H226-H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is an organic compound with the formula C5H9ClO2. It was first synthesized in the mid-20th century as part of research into chlorinated esters and their potential applications. The compound is typically produced by the esterification of 4-chlorobutyric acid with methanol, a process facilitated by acid catalysts. In organic synthesis, methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is used as a key intermediate. Its structure, featuring both an ester and a chloroalkyl group, makes it highly reactive and suitable for various chemical transformations. It can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, where the chlorine atom is replaced by different nucleophiles, allowing the synthesis of a wide range of compounds. The ester group can also be hydrolyzed to produce 4-chlorobutyric acid, which is used in further chemical syntheses. In the pharmaceutical industry, methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is used to synthesize active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. For instance, it can be converted into ?-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogs, which are important in the treatment of neurological disorders such as epilepsy and anxiety. Methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is employed in the agrochemical sector to produce herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. The compound's chlorinated ester structure allows for the development of agrochemicals with specific biological activities, targeting particular pests or pathogens while minimizing harm to the crops. In materials science, methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is used in the synthesis of polymers and resins. Its reactivity with various monomers can create polymers with unique properties, such as enhanced durability and chemical resistance. These materials are used in coatings, adhesives, and other applications where performance and longevity are critical. The compound's ability to introduce functional groups into polymer chains makes it a useful component in developing advanced materials. Methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is utilized in academic and industrial research to explore new synthetic methodologies and reaction mechanisms. Researchers use it as a model compound to study substitution reactions, esterification, and other organic processes. In the flavor and fragrance industry, methyl 4-chlorobutyrate is used as an intermediate to synthesize aroma compounds. Its derivatives can impart fruity and floral notes, enhancing the sensory qualities of various products, including perfumes, food additives, and personal care items. References 2011. Consecutive Reactions with Sulfoximines: Straightforward Synthesis of Substituted 5,5-Spiroketals. Synthesis, 2011(17). DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1260039 1987. Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene by normal ω-chloroalkanoic acids and their methyl esters and nitriles. Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of chemical science, 36(2). DOI: 10.1007/bf00959375 1982. Glass capillary gas chromatography of chlorinated methyl acetates, propanoates and butanoates on Carbowax 20M and SE-30 columns. Chromatographia, 15(8). DOI: 10.1007/bf02260284 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl 4-chlorobutyrate |