Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Blood system medication >> Leukocyte proliferative drug |
|---|---|
| Name | Caffeic acid |
| Synonyms | 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 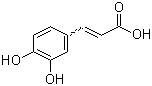 |
| Molecular Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 331-39-5 |
| EC Number | 206-361-2 |
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1/C=C/C(=O)O)O)O |
| Melting point | 194-198 ºC (dec.) |
|---|---|
| Water solubility | soluble in hot water |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335-H351-H361 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305+P351+P338 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Caffeic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound that belongs to the class of hydroxycinnamic acids. It is widely found in various plants and is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin and other important plant metabolites. Caffeic acid was first isolated from plants in the early 20th century. Its name is derived from "caffeine", reflecting its association with coffee and related plants. Researchers discovered caffeic acid while studying the chemical composition of coffee beans and subsequently found it to be a major component of many fruits, vegetables and grains. Its presence in large quantities in coffee, wine and propolis has attracted the attention of the scientific community for its potential health benefits and industrial applications. Caffeic acid has several notable properties. Its chemical formula is C9H8O4, its molecular weight is 180.16 g/mol, and it is a yellow crystalline solid. It is soluble in water, ethanol and methanol. It is a powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals and reduces oxidative stress. Caffeic acid has been widely studied for its potential health benefits. Its antioxidant properties help prevent chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Studies have shown that caffeic acid can inhibit tumor growth and enhance immune response. It also has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making it valuable in the development of therapeutics and dietary supplements. The cosmetics industry takes advantage of caffeic acid’s skin-protective properties. Its antioxidant activity helps prevent skin damage caused by UV rays and pollution. Caffeic acid is added to skin care products to reduce signs of aging, improve skin texture, and promote a healthy complexion. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties help soothe irritated skin and reduce redness. Caffeic acid is used in the food industry as a natural preservative and flavoring agent. Its antioxidant properties prevent oxidation and spoilage, thereby extending the shelf life of foods. It is commonly found in coffee, wine, and various fruits and vegetables, helping to enhance their flavor and nutritional value. Caffeic acid’s role in enhancing food’s sensory properties and stability makes it a valuable additive. In agriculture, caffeic acid is recognized for its role in plant defense mechanisms. It helps plants fight off pathogens and pests by strengthening cell walls and acting as a precursor to various defense compounds. Researchers are exploring its potential as a natural pesticide and growth promoter to reduce reliance on synthetic chemicals and enhance sustainable agricultural practices. Caffeic acid is a key compound in pharmaceutical research. Its ability to interact with various biological pathways makes it a valuable model for studying disease mechanisms and developing new drugs. Researchers are investigating its potential to modulate enzyme activity, influence gene expression, and interact with cell receptors, paving the way for new therapeutic approaches. The future of caffeic acid research is promising, with ongoing studies exploring its full range of biological activities and potential applications. Advances in extraction and synthesis methods are expected to increase its availability and reduce production costs. The development of caffeic acid derivatives with improved efficacy and stability will further expand its use in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. References Horbury, M. D., et al., 2016. Photodynamics of potent antioxidants: ferulic and caffeic acids. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 18, 17697. DOI: 10.1039/C6CP01595F Thirupathi Kumara Raja, S., et al., 2015. In vitro and in vivo assessments of a 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid bioconjugated gelatin-based injectable hydrogel for biomedical applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 3, 1244. DOI: 10.1039/C4TB01196A Andrade, M., et al., 2015. Fine-tuning of the hydrophobicity of caffeic acid: studies on the antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. RSC Advances, 5, 53925. DOI: 10.1039/C5RA05840F |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Caffeic acid |