Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Suzhou Biosyntech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13921151340 +86 (512) 6300-1269 | |||
 |
sales2@biosyntech-suzhou.com sales@biosyntech-suzhou.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2019 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2020 | ||||
| Classification | Pharmaceutical intermediate >> Heterocyclic compound intermediate >> Pyridazine |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl (S)-Hexahydropyridazine-3-carboxylate Hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | methyl (3S)-diazinane-3-carboxylate;hydrochloride |
| Molecular Structure | 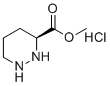 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13ClN2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 180.63 |
| CAS Registry Number | 380223-17-6 |
| SMILES | COC(=O)[C@@H]1CCCNN1.Cl |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P301+P312-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
Methyl (S)-hexahydropyridazine-3-carboxylate hydrochloride is a chiral, nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound used as an intermediate in medicinal chemistry and synthetic organic chemistry. The compound consists of a six-membered saturated pyridazine ring with nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 2, a methyl ester at the 3-position, and is present as a hydrochloride salt to enhance stability and solubility. The (S)-configuration at the 3-position provides a defined stereocenter, which is important for stereoselective reactions and for incorporation into chiral molecules in drug discovery. This intermediate is commonly employed in multi-step synthesis where a chiral hexahydropyridazine core is required. The ester functionality enables derivatization through hydrolysis, amidation, or reduction reactions, allowing its transformation into amides, acids, or alcohols. The hydrochloride salt form improves handling by providing a crystalline solid that is more resistant to racemization and easier to weigh and store under standard laboratory conditions. In medicinal chemistry, methyl (S)-hexahydropyridazine-3-carboxylate hydrochloride is utilized for the construction of heterocyclic scaffolds in small-molecule therapeutics. Its stereochemistry and functional groups allow for selective coupling and elaboration, facilitating the synthesis of pharmacologically active compounds with specific three-dimensional orientations. Proper handling includes storage in a cool, dry place to prevent decomposition, and analytical techniques such as NMR, mass spectrometry, and chiral HPLC are used to confirm purity and stereochemical integrity. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl (S)-Hexahydropyridazine-3-carboxylate Hydrochloride |