Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hangzhou Ich Biofarm Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 2818-6870 | |||
 |
specialchem1@ichemie.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Medilink Pharmachem | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 (79) 3007-0133 | |||
 |
exports@medilinkpharma.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 1996 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2014 | ||||
| Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (852) 3060-6658 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Finetech Industry Limited | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (27) 8746-5837 +86 18971612321 | |||
 |
sales@finetechnology-ind.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2009 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2019 | ||||
| LKT Laboratories, Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (888) 558-5227 | |||
 |
peacerli@mbolin-lktlabs.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Cayman Chemical Company | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (734) 971-3335 | |||
 |
sales@caymanchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | API >> Other chemicals |
|---|---|
| Name | Bupivacaine |
| Synonyms | 1-Butyl-2',6'-pipecoloxylidide; 1-Butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide; Anekain; Bucain |
| Molecular Structure | 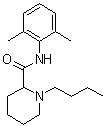 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H28N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 288.43 |
| CAS Registry Number | 38396-39-3 |
| EC Number | 253-911-2 |
| SMILES | CCCCN1CCCCC1C(=O)NC2=C(C=CC=C2C)C |
| Density | 1.032±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr), Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 110 ºC** |
| Boiling point | 423.4±45.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 209.9±28.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.547 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software V11.02 (©1994-2015 ACD/Labs) |
| ** | Luduena, Froilan P.; ZA 6802611 1968. |
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bupivacaine is a widely used local anesthetic of the amide type, commonly employed in clinical settings for regional anesthesia, including epidural, spinal, and peripheral nerve blocks. Its chemical name is (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide, with a molecular formula of C18H28N2O. Bupivacaine is characterized by a lipophilic aromatic ring system attached to a piperidine ring linked through an amide bond, which contributes to its potency and duration of action. The compound was first synthesized in the 1950s and introduced into clinical practice in the 1960s as a longer-acting alternative to earlier local anesthetics such as lidocaine. Bupivacaine's ability to provide prolonged anesthesia and analgesia with relatively low systemic toxicity made it a preferred choice for surgical procedures and labor analgesia. Bupivacaine functions by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve membranes, preventing the initiation and propagation of nerve impulses. This blockade inhibits sensory and motor nerve transmission, resulting in localized loss of sensation and muscle relaxation. Its high lipid solubility enhances membrane penetration and binding affinity, contributing to its potency and long duration. The drug exists as a racemic mixture of R- and S-enantiomers; however, the S-enantiomer, known as levobupivacaine, has been developed and marketed due to its improved safety profile and reduced cardiotoxicity. Bupivacaine's cardiotoxic effects are mainly attributed to the R-enantiomer, and the development of levobupivacaine allows clinicians to minimize these adverse effects while maintaining anesthetic efficacy. Bupivacaine is typically administered as a hydrochloride salt in aqueous solution. Its onset of action ranges from 2 to 10 minutes, and the duration can extend from 2 to 8 hours depending on the dose, site of administration, and presence of vasoconstrictors. The drug is metabolized primarily in the liver via N-dealkylation by cytochrome P450 enzymes, and metabolites are excreted renally. Clinically, bupivacaine is utilized for a variety of procedures, including dental work, orthopedic surgeries, cesarean sections, and postoperative pain management. Its prolonged effect reduces the need for repeated dosing and continuous infusions. However, care must be taken to avoid systemic toxicity, which can manifest as central nervous system symptoms (such as tinnitus, seizures) and cardiovascular complications (such as arrhythmias and cardiac arrest). Pharmacological research continues to explore formulations and delivery methods to optimize bupivacaine’s efficacy and safety, including liposomal encapsulation and combined use with adjuvants. Such advances aim to extend analgesia duration while minimizing peak plasma concentrations to reduce toxicity risk. In summary, bupivacaine is a potent amide local anesthetic with a long duration of action, widely used in medical practice for regional anesthesia and analgesia. Its chemical structure and pharmacodynamic properties underlie its clinical effectiveness and challenges, driving ongoing development for safer and more effective anesthetic agents. References 2024. The anesthetic and recovery profiles of low-dose hypobaric mepivacaine and bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia in total hip and knee arthroplasty: a prospective observational study. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d'anesthésie. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-024-02887-y 2024. Preoperative Analgesia Efficacy of Liposomal Bupivacaine Following Pericapsular Nerve Group (PENG) Block in Patients with Hip Fracture: A Randomized Controlled Observer-Blinded Study. Pain and Therapy. DOI: 10.1007/s40122-024-00683-6 2024. Ultrasound-guided obturator nerve block technique at the distal end of the obturator canal: case series and cadaver evaluation. Journal of Anesthesia. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-024-03434-1 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Bupivacaine |