Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Alfa Chemistry | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (201) 478-8534 | |||
 |
inquiry@alfa-chemistry.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2012 | ||||
| Hangzhou Leap Chem Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8771-1850 | |||
 |
market19@leapchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2006 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Shanghai Fuxin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (21) 3130-0828 +86 18645121291 | |||
 |
contact@fuxinpharm.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2018 | ||||
| Chemical Bull Private Limited | India | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+91 96969 60250 | |||
 |
info@chemicalbull.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2016 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2022 | ||||
| Xinlian Rui Biomedical Technology (shandong) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 15153173989 | |||
 |
3865799121@qq.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 15153173989 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2024 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| P and M Invest Ltd. | Russia | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+7 (495) 135-6494 | |||
 |
sales@fluorine1.ru | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Hansa Fine Chemicals GmbH | Germany | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+49 (421) 427-682 | |||
 |
jbarten@hfc-chemicals.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Fatty ketone (including enol) |
|---|---|
| Name | 1,1-Difluoro-2-propanone |
| Synonyms | 1,1-Difluoroacetone; 1,1-Difluoropropan-2-one |
| Molecular Structure | 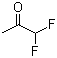 |
| Molecular Formula | C3H4F2O |
| Molecular Weight | 94.060 |
| CAS Registry Number | 431-05-0 |
| EC Number | 688-420-6 |
| SMILES | CC(=O)C(F)F |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.164 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 45.3±25.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 46.1 - 47.1 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 1.6±17.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.302 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS02;GHS07 DangerGHS02;GHS02 Details
GHS02;GHS07 DangerGHS02;GHS02 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H225-H226-H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P233-P240-P241-P242-P243-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P370+P378-P403+P233-P403+P235-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1,1-Difluoro-2-propanone is a small fluorinated ketone with the molecular formula CF2CHCOCH3. It belongs to the class of geminal difluoroketones, in which two fluorine atoms are attached to the same carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl group. The introduction of the difluoromethyl group significantly alters the electronic properties of the molecule, increasing the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon and stabilizing adjacent intermediates. The compound is typically a colorless liquid under standard conditions and is reactive due to the combined effects of the carbonyl and difluoromethyl functionalities. The discovery of 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone is linked to the mid-20th century development of organofluorine chemistry, when chemists sought to explore the influence of fluorine substitution on carbonyl compounds. Fluorinated ketones like this one were of particular interest due to their enhanced chemical stability, altered acidity of adjacent protons, and unique reactivity in nucleophilic and condensation reactions. The compound provides a versatile platform for introducing difluoromethyl groups into more complex organic molecules. In synthetic chemistry, 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone is used as a building block for the preparation of fluorinated intermediates. Its carbonyl group allows for reactions such as nucleophilic addition, condensation, and reduction, while the difluoromethyl group stabilizes resulting products and influences reactivity. This makes the compound valuable for synthesizing difluoromethylated alcohols, amines, and heterocycles, which are important in medicinal chemistry and agrochemical applications. In pharmaceutical research, derivatives of 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone are used to incorporate difluoromethyl groups into drug candidates. The difluoromethyl moiety can act as a bioisostere for hydroxyl or methyl groups, enhancing metabolic stability, lipophilicity, and overall pharmacokinetic properties. The ketone functionality allows selective modification and derivatization, making it useful for the preparation of enzyme inhibitors, antiviral agents, and other bioactive compounds. In agrochemicals, 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone has been employed as an intermediate for the synthesis of herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides. The electron-withdrawing difluoromethyl group enhances chemical stability and biological activity, enabling the design of compounds with improved efficacy and environmental persistence. The compound also finds application in materials science and specialty chemical synthesis. Fluorinated intermediates derived from 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone are used to introduce difluoromethyl groups into polymers, coatings, and other functional materials, where fluorination improves hydrophobicity, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. The development and use of 1,1-difluoro-2-propanone highlight its role as a versatile fluorinated building block in modern chemistry. Its unique combination of a reactive carbonyl group and a stabilizing difluoromethyl substituent makes it an important tool in organic synthesis, pharmaceutical development, agrochemical production, and materials science. The compound exemplifies how selective fluorination can enhance reactivity, stability, and functional utility in small organic molecules. References 2017. Characterization of two carbonyl reductases from Ogataea polymorpha NBRC 0799. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 101(24). DOI: 10.1007/s00253-017-8668-8 2007. Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate as a Metal-Free, Homogeneous and Strong Lewis Acid Catalyst for Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of a-Aminonitriles and Their Fluorinated Analogues. Synlett, 2007(16). DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-985594 2016. Synthesis of LpxC Inhibitor LP-058. Synfacts, 12(07). DOI: 10.1055/s-0035-1562373 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1,1-Difluoro-2-propanone |