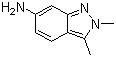
2,3-Dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole is an organic compound with a unique structure that has attracted attention in various fields of chemical research. 2,3-Dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole was first synthesized in the mid-20th century as part of a study to explore new indazole derivatives. The unique structural features of this compound, including two methyl groups and one amino group on the indazole ring, have made it a subject of interest for its potential applications in medicinal chemistry and materials science. It has a molecular formula of C10H12N4 and a molecular weight of 172.23 g/mol. It is an off-white to light brown crystalline solid. It has a melting point of about 200-205°C and is slightly soluble in water and more soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and acetone. The structure of this compound has a fused indazole ring system with two methyl groups and one amino group, which gives it unique chemical and biological properties.
2,3-Dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole has been explored for its potential pharmaceutical applications. Its structure is similar to other biologically active compounds, making it a candidate for development as a drug or therapeutic agent. Research focuses on its ability to interact with biological targets such as enzymes and receptors, which could lead to new treatments for various diseases.
In chemical research, 2,3-dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole is used as a building block for the synthesis of more complex molecules. Its unique structure allows chemists to explore new synthetic routes and develop innovative compounds with potential applications in medicine and materials science. It is a useful intermediate in the design of new indazole derivatives.
The unique properties of this compound make it valuable in materials science. It is studied for its potential use in the development of advanced materials such as organic semiconductors and dyes. Its ability to form stable complexes with various metals and other organic compounds can be used to create materials with specific electronic and optical properties.
Researchers use 2,3-dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole to study its biological effects and mechanisms of action. Its interactions with biological systems are important for understanding its potential as a bioactive compound. Research aims to elucidate its effects on cellular processes, which can provide insights into its potential therapeutic applications.
In pharmacological studies, 2,3-dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole has been screened for various biological activities, including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. These studies have helped identify it as a lead compound for drug development and evaluate its efficacy and safety in preclinical models.
The future of 2,3-dimethyl-6-amino-2H-indazole research is promising, with ongoing studies exploring its full range of applications and optimizing its properties. Advances in synthetic techniques and biological screening methods are expected to increase the utility of this compound in a variety of areas. Continued research may uncover new applications.
|



















 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details