Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | API >> Circulatory system medication >> Antiarrhythmic drug |
|---|---|
| Name | Carteolol hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | Endak; Mikelan; NSC 300906; OC 1085; OPC 1085; Ocupress; Optipress; Tenalet; Tenalin; Teoptic; 5-(3-tert-Butylamino-2-hydroxy)propoxy-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril hydrochloride |
| Molecular Structure | 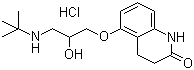 |
| Molecular Formula | C16H24N2O3.HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 328.83 |
| CAS Registry Number | 51781-21-6 |
| EC Number | 257-415-7 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)NCC(COC1=CC=CC2=C1CCC(=O)N2)O.Cl |
| Melting point | 278 ºC (Expl.)* |
|---|---|
| Solubility | DMSO:43mg/mL (Expl.) |
| * | "Drugs - Synonyms and Properties" data were obtained from Ashgate Publishing Co. (US) |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H319-H351-H361 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P264-P264+P265-P270-P280-P301+P317-P305+P351+P338-P318-P330-P337+P317-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Carteolol hydrochloride is a synthetic pharmaceutical compound belonging to the class of beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists, commonly known as beta blockers. Chemically, it is a cardioselective beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptor antagonist with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), which differentiates it from some other beta blockers by its partial agonist properties at beta receptors. The compound is formulated as the hydrochloride salt to enhance its solubility and stability for pharmaceutical use. Carteolol hydrochloride was developed in the latter half of the 20th century and has been widely used since the 1980s, particularly in ophthalmology for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure associated with glaucoma and ocular hypertension. It is marketed under various brand names worldwide and is administered mainly as an ophthalmic solution. The mechanism of action of carteolol hydrochloride involves non-selective blockade of beta-adrenergic receptors in the eye, leading to decreased production of aqueous humor by the ciliary body. This reduction in aqueous humor lowers intraocular pressure, which is critical in managing glaucoma to prevent optic nerve damage and consequent vision loss. Unlike some other beta blockers used for glaucoma, carteolol exhibits ISA, which may reduce the incidence of adverse effects such as bradycardia and bronchospasm. Pharmacokinetically, carteolol hydrochloride applied topically to the eye exhibits good corneal penetration and ocular bioavailability. Systemic absorption occurs but is limited, reducing the likelihood of systemic beta-blockade side effects. The drug undergoes hepatic metabolism and is excreted primarily via the kidneys. In addition to its ophthalmic use, carteolol hydrochloride has been prescribed systemically as an antihypertensive and antianginal agent. Its ISA confers some advantages by avoiding excessive slowing of heart rate and allowing maintenance of basal sympathetic tone. Adverse effects associated with carteolol hydrochloride are generally mild but can include local ocular irritation, dry eyes, and transient blurred vision. Systemic effects, though uncommon with topical administration, may include bradycardia, hypotension, and bronchospasm, especially in susceptible individuals such as asthmatics. Therefore, caution is advised when prescribing carteolol to patients with respiratory diseases or cardiac conduction abnormalities. Chemical characterization of carteolol hydrochloride involves spectroscopic techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS), which confirm its molecular structure and purity. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy provides information about functional groups, including the secondary amine and aromatic ether moieties. The compound is typically a white to off-white crystalline powder, soluble in water due to the hydrochloride salt form. Analytical methods for the quantitative determination of carteolol hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulations and biological fluids include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet (UV) detection and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), enabling sensitive and specific measurement for quality control and pharmacokinetic studies. In clinical practice, carteolol hydrochloride is administered as eye drops in concentrations commonly ranging from 1% to 2%. The dosing regimen typically involves one to two drops applied to the affected eye(s) once or twice daily, depending on the severity of intraocular pressure elevation and patient response. In summary, carteolol hydrochloride is a non-selective beta blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity primarily used as an ophthalmic agent to reduce intraocular pressure in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Its pharmacological profile, combining effective beta-adrenergic blockade with partial agonism, provides therapeutic benefits while mitigating some side effects seen with other beta blockers. The compound’s established safety and efficacy have made it a valuable option in ocular pharmacotherapy. References 2023. Urinary excretion patterns and potential risks of beta-blocker ophthalmic drops in sports. Drug Testing and Analysis, 14(11). DOI: 10.1002/dta.3368 2023. Carteolol triggers senescence via activation of β-arrestin�ERK�NOX4�ROS pathway in human corneal endothelial cells in vitro. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 379. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110511 2022. Beta-blocker carteolol and oxprenolol produce cutaneous analgesia in response to needle pinpricks in the rat. Neurological Research, 44(11). DOI: 10.1080/01616412.2022.2148511 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Carteolol hydrochloride |