Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Auben Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 19121901603 | |||
 |
sales@aubenchem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2023 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Carboxylic compounds and derivatives >> Carboxylic esters and their derivatives |
|---|---|
| Name | Methyl 5-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzoate |
| Molecular Structure | 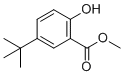 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H16O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 208.25 |
| CAS Registry Number | 52888-72-9 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)C(=O)OC |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 287.8±28.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 113.5±16.8 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.518 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H318-H335 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P270-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P310-P330-P332+P313-P362-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details |
|
Methyl 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoate is an organic compound belonging to the class of substituted hydroxybenzoate esters. Its molecular formula is C12H16O3, and it is a methyl ester of 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoic acid. The compound contains three main substituents on the benzene ring: a hydroxyl group at the 2‑position, a methyl ester group at the carboxylate, and a tert‑butyl group at the 5‑position. The hydroxyl group adjacent to the ester is characteristic of salicylate derivatives, which are known for their chemical reactivity and potential antioxidant properties. The tert‑butyl substituent on the aromatic ring contributes steric bulk, increasing stability and influencing the reactivity of the phenolic hydroxyl. Bulky substituents on phenolic compounds are known to stabilize phenoxyl radicals formed upon hydrogen donation, which underpins their function as antioxidants. Methyl 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoate is structurally related to hindered phenol antioxidants widely used in the stabilization of polymers, fuels, and other materials, providing insight into the influence of steric hindrance on radical scavenging efficiency. The compound can be synthesized through esterification of the corresponding carboxylic acid, 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoic acid, with methanol under acid catalysis. This reaction proceeds via protonation of the carbonyl oxygen, nucleophilic attack by methanol, and elimination of water to yield the methyl ester. Reaction conditions, including temperature and catalyst choice, influence the yield and purity. Esterification of substituted hydroxybenzoic acids is a common method to prepare methyl esters as intermediates or final products for chemical research. Methyl 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoate serves as a useful building block in synthetic chemistry and materials science. The ester group can undergo further transformations, such as hydrolysis to the corresponding acid, amidation, or transesterification, enabling preparation of derivatives with tailored properties. The hydroxyl group at the 2‑position can participate in hydrogen bonding and can be modified through etherification or acylation reactions. The combination of the bulky tert‑butyl group and the reactive ester and hydroxyl functionalities allows for selective chemical modifications while preserving the integrity of the aromatic ring. Physically, the compound is a colorless or light yellow solid. It is soluble in common organic solvents such as ethanol, methanol, and diethyl ether, while solubility in water is limited. The presence of the tert‑butyl group and ester functionality contributes to thermal stability, although prolonged exposure to light or oxygen can cause oxidation and discoloration. These properties are consistent with other phenolic esters and make the compound suitable for laboratory handling and storage. In industrial and research contexts, methyl 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoate is used as a model compound for studying steric effects in phenolic antioxidants. Derivatives of hydroxybenzoate esters are often incorporated into polymers and coatings to prevent oxidative degradation. The structure’s combination of a free phenolic hydroxyl and sterically hindering tert‑butyl group exemplifies how chemical modifications influence reactivity and antioxidant performance. Overall, methyl 5‑tert‑butyl‑2‑hydroxybenzoate demonstrates how the design of substituted hydroxybenzoate esters can combine chemical stability, functional versatility, and steric protection. Its structure allows for selective transformations at both the hydroxyl and ester groups while providing insight into the behavior of hindered phenols in synthetic and materials chemistry. The compound is a valuable reagent for laboratory synthesis and research into antioxidant mechanisms and structure–activity relationships. |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methyl 5-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzoate |