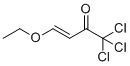
(E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Its unique structure and properties have attracted interest for various applications in organic synthesis and material science. The compound was first synthesized in the late 20th century, a period characterized by significant advancements in organic chemistry, particularly in the development of synthetic methodologies for producing halogenated compounds. The synthesis of (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one typically involves the reaction of 1,1,1-trichloroacetone with ethyl vinyl ether in the presence of a suitable catalyst, leading to the formation of the desired product.
The distinct characteristics of (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one stem from its halogenated structure, which imparts unique reactivity patterns, making it a valuable intermediate in various chemical transformations. One of the primary applications of this compound is in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules. Its electrophilic nature allows it to participate in nucleophilic addition reactions, leading to the formation of diverse functional groups. This property has made it useful in the pharmaceutical industry, where it serves as a building block for developing new therapeutic agents.
In addition to its use in organic synthesis, (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one has applications in material science. The compound can be employed in the production of specialty polymers and resins due to its ability to undergo polymerization reactions. By incorporating this compound into polymer matrices, researchers can tailor the material properties, such as thermal stability and mechanical strength, enhancing the performance of various applications, including coatings and adhesives.
Another significant application of (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one is in agrochemical formulations. The compound has shown potential as an intermediate in the synthesis of agrochemicals, including pesticides and herbicides. Its reactivity can be harnessed to develop novel agrochemical agents that offer improved efficacy and selectivity, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices.
Research into the environmental impact and safety of (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one is ongoing, particularly concerning its degradation pathways and potential toxicity. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring that the compound can be used safely in various applications without posing risks to human health or the environment. The development of green chemistry approaches for synthesizing and utilizing this compound is also an area of interest, aiming to minimize waste and energy consumption while maximizing efficiency.
As the demand for innovative chemical products continues to rise, the significance of (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one in various industrial applications is likely to grow. Its versatility as a synthetic intermediate and its potential use in material science and agrochemicals position it as an important compound in the field of organic chemistry. Ongoing research efforts focused on optimizing its synthesis and expanding its applications will further enhance its relevance in modern chemical processes.
In summary, (E)-1,1,1-trichloro-4-ethoxybut-3-en-2-one is a valuable compound in organic synthesis, material science, and agrochemicals. Its unique properties and reactivity patterns make it an essential intermediate for developing various chemical products. As research continues, the understanding of this compound’s applications and safety will evolve, ensuring its effective use in multiple domains.
|









 GHS02;GHS05;GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS02;GHS05;GHS06;GHS07 Danger Details