Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
|
CAS: 60561-17-3 Product: Sufentanil citrate No suppilers available. |
| Classification | Analytical chemistry >> Standard >> Standard material |
|---|---|
| Name | Sufentanil citrate |
| Synonyms | R 30730 citrate salt; R 33800; Sufenta; Sufentanil forte; Sufentanyl citrate |
| Molecular Structure | 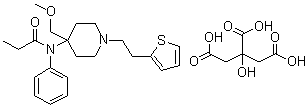 |
| Molecular Formula | C22H30N2O2S.C6H8O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 578.68 |
| CAS Registry Number | 60561-17-3 |
| EC Number | 262-295-4 |
| SMILES | CCC(=O)N(C1=CC=CC=C1)C2(CCN(CC2)CCC3=CC=CS3)COC.C(C(=O)O)C(CC(=O)O)(C(=O)O)O |
| Solubility | 1 mg/mL (H2O), 50 mM (DMSO), 20 mM (ethanol) (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS06 Danger Details
GHS06 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H300-H300-H310-H330 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P262-P264-P270-P271-P280-P284-P301+P316-P302+P352-P304+P340-P316-P320-P321-P330-P361+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Controlled Substance | DEA Drug Code Number: 9740 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSA Schedule: II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Narcotics? Yes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sufentanil citrate is a highly potent synthetic opioid analgesic used primarily in clinical anesthesia and intensive care settings. It is a derivative of fentanyl, with structural modifications that enhance its binding affinity to the µ-opioid receptor, leading to significantly greater potency. Sufentanil is approximately 5 to 10 times more potent than fentanyl and 500 to 1,000 times more potent than morphine on a per weight basis. The compound was developed to provide rapid-onset, short-duration analgesia with a favorable pharmacokinetic profile for controlled use during surgery and in critical care. Sufentanil citrate is the water-soluble salt form, which allows for precise dosing in intravenous and epidural administration. Its lipophilic nature contributes to fast penetration of the central nervous system, making it suitable for induction and maintenance of anesthesia, particularly when hemodynamic stability is essential. Clinically, sufentanil citrate is administered as part of balanced anesthesia, often in combination with sedative-hypnotics and muscle relaxants. It is also used in monitored anesthesia care and for epidural analgesia during labor and postoperative pain management. Due to its potency, dosing is carefully calibrated to avoid respiratory depression and other opioid-related adverse effects. The drug has a rapid onset of action, typically within minutes, and a context-sensitive half-life that makes it suitable for continuous infusion. Sufentanil exhibits high receptor selectivity for μ-opioid receptors, producing profound analgesia, sedation, and suppression of the stress response. Unlike morphine and other longer-acting opioids, it has minimal histamine release, reducing the risk of hypotension and allergic-type reactions during administration. Its short duration of action allows for rapid emergence from anesthesia, which is particularly useful in outpatient or short-stay surgical procedures. The pharmacokinetics of sufentanil are influenced by hepatic metabolism through N-dealkylation and O-demethylation, primarily mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. The metabolites are excreted in the urine, and accumulation may occur in patients with impaired liver or kidney function. Close monitoring is required during prolonged administration, especially in intensive care settings. The drug’s therapeutic use is tightly regulated due to its high potency and potential for misuse. It is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance in many jurisdictions. While its abuse in illicit contexts is less common than fentanyl or carfentanil, sufentanil remains a target of concern in opioid diversion and overdose prevention efforts. Advancements in delivery systems, including sublingual formulations, have expanded the clinical applications of sufentanil in recent years, particularly for acute pain management in military and emergency medicine. However, its use outside of controlled environments is limited due to the narrow margin between therapeutic and toxic doses. Sufentanil citrate continues to be a valuable tool in modern anesthetic practice, offering high efficacy in pain control with rapid onset and manageable duration. Its use requires experienced clinical oversight to ensure safety, particularly given the risks associated with opioid-induced respiratory depression and the need for effective reversal agents in overdose situations. References 1990. Transdermal Delivery of Narcotic Analgesics: pH, Anatomical, and Subject Influences on Cutaneous Permeability of Fentanyl and Sufentanil. Pharmaceutical Research, 7(8). DOI: 10.1023/a:1015912932416 1998. Intrathecal Clonidine Combined with Sufentanil for Labor Analgesia. Anesthesiology, 88(3). DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199803000-00015 2000. Fentanyl versus sufentanil: plasma concentrations during continuous epidural postoperative infusion in children. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 85(4). DOI: 10.1093/bja/85.4.615 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Sufentanil citrate |