Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Organic raw materials >> Amino compound >> Acyclic monoamines, polyamines and their derivatives and salts |
|---|---|
| Name | Methylamine |
| Synonyms | Monomethylamine |
| Molecular Structure | 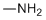 |
| Molecular Formula | CH5N |
| Molecular Weight | 31.06 |
| CAS Registry Number | 74-89-5 |
| EC Number | 200-820-0 |
| SMILES | CN |
| Density | 0.6±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 0.7 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -93 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | -21.1±3.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, -6.3 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | -65.9±13.1 ºC (Calc.)*, -13.9 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | soluble (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.34 (Calc.)*, 1.37 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |



 GHS02;GHS04;GHS05;GHS07 DangerGHS02 Details
GHS02;GHS04;GHS05;GHS07 DangerGHS02 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H220-H315-H318-H332-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P210-P222-P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P317-P319-P321-P332+P317-P362+P364-P377-P381-P403-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 1061 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Methylamine is the simplest primary aliphatic amine, with the chemical formula CH₃NH₂. It consists of a methyl group (-CH₃) attached to an amino group (-NH₂), making it structurally and chemically intermediate between ammonia and higher amines. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas with a strong, ammonia-like odor, highly soluble in water and commonly handled as a 40% aqueous solution or compressed gas. Methylamine is industrially synthesized by the reaction of methanol and ammonia over an aluminosilicate catalyst at elevated temperatures and pressures. This process yields a mixture of methylamine, dimethylamine, and trimethylamine. The proportion of each product can be adjusted by controlling the ammonia-to-methanol ratio. In organic synthesis, methylamine is widely used due to its nucleophilicity and basicity. It undergoes acylation, alkylation, and condensation reactions readily. As a nucleophile, it reacts with electrophilic carbon centers to form C–N bonds, enabling the construction of amides, imines, and various nitrogen-containing heterocycles. Methylamine has extensive applications across multiple industries. In pharmaceuticals, it is a precursor to various drug molecules, including local anesthetics, bronchodilators, and antihistamines. It also serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of methamphetamine, which is strictly regulated due to abuse potential. In agrochemicals, methylamine is involved in producing herbicides, such as atrazine, and insecticides. It is used in tanning agents and surfactants and as a building block for water treatment chemicals. It also finds use in the electronics industry for etching semiconductors and in the manufacture of rocket propellants. From a safety perspective, methylamine is flammable and toxic. Inhalation can cause respiratory tract irritation, and high concentrations may lead to systemic toxicity. It reacts violently with oxidizing agents and acids. Therefore, it must be handled with appropriate protective measures, including ventilation, gas detection systems, and fire suppression protocols. Due to its involvement in illicit drug manufacture, methylamine is a controlled substance in several jurisdictions. However, it remains a valuable reagent in legal industrial and laboratory processes, particularly for its simplicity, reactivity, and low molecular weight. Methylamine plays a pivotal role in both academic research and industrial chemistry. It offers a fundamental example of amine reactivity and continues to be an indispensable tool in synthetic methodologies, from small-scale laboratory procedures to large-scale chemical manufacturing. References 1991. Effects of cytochalasin D and methylamine on intracellular growth of Legionella pneumophila in amoebae and human monocyte-like cells. Infection and Immunity, 59(3). DOI: 10.1128/iai.59.3.758-763.1991 1991. Weak base amines can inhibit class I MHC-restricted antigen presentation. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 146(2). DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.146.2.449 1984. Methylation of DNA in stomach and small intestine of rats after oral administration of methylamine and nitrite. Carcinogenesis, 5(12). DOI: 10.1093/carcin/5.12.1729 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Methylamine |