Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Hangzhou Yanshan Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8689-7279 8669-6867 | |||
 |
sales@yanshan-chem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Jiangxi Anlida Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (577) 8837-7057 | |||
 |
sandyfan@anlidachem.cn | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1991 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2011 | ||||
| Alchemie Shanghai Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (021) 5072-0087 | |||
 |
assistant2@alchemie-shanghai.com | |||
| Chemical distributor since 2018 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Crescent Chemical Co. Inc. | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 348-0333 | |||
 |
crescent@creschem.com | |||
| Chemical distributor | ||||
| Classification | Analytical chemistry >> Standard >> Pesticides, veterinary drugs and fertilizers |
|---|---|
| Name | Aclonifen |
| Synonyms | 2-Chloro-6-nitro-3-phenoxyaniline |
| Molecular Structure | 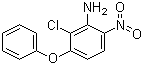 |
| Molecular Formula | C12H9ClN2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 264.66 |
| CAS Registry Number | 74070-46-5 |
| EC Number | 277-704-1 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)OC2=C(C(=C(C=C2)[N+](=O)[O-])N)Cl |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 361.5±42.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 172.4±27.9 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.656 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |


 GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS08;GHS09 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H317:-H351:-H400:-H410: Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P203-P261-P272-P273-P280-P302+P352-P318-P321-P333+P317-P362+P364-P391-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aclonifen is a pre-emergence herbicide widely used for controlling broadleaf and some grass weeds in crops such as potatoes, sunflowers, and legumes. Belonging to the chemical family of diphenyl ethers, aclonifen is characterized by its distinct mode of action, which primarily interferes with carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. This inhibition disrupts chloroplast development, leading to a bleaching effect in susceptible weed seedlings and ultimately causing their death before or shortly after emergence. Chemically, aclonifen is 2-chloro-6-nitro-3-phenoxyaniline. Its mode of action is classified under the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) Group F3, which targets the enzyme involved in phytoene desaturase (PDS) activity during carotenoid biosynthesis. This mode is different from photosystem II inhibitors, making aclonifen a useful option in resistance management programs, especially in areas where other herbicide modes of action have become less effective due to resistance development. Aclonifen is typically applied as a soil-surface spray before crop emergence. Its efficacy is influenced by factors such as soil moisture, texture, and organic matter content, as these affect the herbicide’s distribution and availability in the upper soil layers where weed seeds germinate. While aclonifen has limited systemic activity, it forms a chemical barrier at the soil surface that inhibits seedling development upon contact. One of the key advantages of aclonifen is its crop selectivity. Many broadacre crops can tolerate it at recommended application rates without adverse effects. This selectivity, combined with long-lasting residual activity, makes it an attractive choice for pre-emergent weed control. It helps maintain early-season weed-free conditions, which are critical for maximizing crop yield potential. Environmental behavior studies show that aclonifen is relatively stable in soil, with moderate persistence depending on soil type and climatic conditions. It has low mobility, which reduces the risk of leaching into groundwater. However, its high affinity for soil organic matter may influence availability and performance under certain field conditions. Aclonifen is generally considered to pose a low risk to non-target organisms when used according to label guidelines, although care must be taken to avoid spray drift into adjacent areas. As part of integrated weed management (IWM) strategies, aclonifen is often used in rotation or combination with other herbicides to reduce the likelihood of resistance development. Although weed resistance to aclonifen is not widespread, proactive stewardship is essential to preserve its effectiveness. In addition to chemical control, cultural practices such as crop rotation, mechanical weeding, and optimal planting density are recommended to enhance the overall effectiveness of weed control programs. Aclonifen's utility has expanded in recent years due to its compatibility with modern agricultural practices and its ability to fill gaps left by declining efficacy of older herbicides. In regulatory terms, its approval and usage conditions vary by region, often governed by environmental risk assessments and residue tolerances established for specific crops. It has gained renewed interest in sustainable agriculture, where herbicide stewardship, crop safety, and resistance management are of increasing importance. References 2022. Aclonifen induces bovine mammary gland epithelial cell death by disrupting calcium homeostasis and inducing ROS production. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 180. DOI: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2021.105011 2022. Aclonifen could induce implantation failure during early embryonic development through apoptosis of porcine trophectoderm and uterine luminal epithelial cells. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 188. DOI: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105288 2023. Study of the degradation of diphenyl-ether herbicides aclonifen and bifenox in different environmental waters. Chemosphere, 335. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139238 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Aclonifen |