Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Xi'an Yuri Solar Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (029) 8110-1199 | |||
 |
jiaop@yurisolar.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: plt18092602675 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2007 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Phosphonate / phosphonate |
|---|---|
| Name | (4-(2,7-Dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 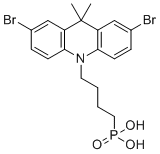 |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22Br2NO3P |
| Molecular Weight | 503.16 |
| CAS Registry Number | 2971088-37-4 |
| EC Number | 987-144-6 |
| SMILES | CC1(C2=C(C=CC(=C2)Br)N(C3=C1C=C(C=C3)Br)CCCCP(=O)(O)O)C |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details |
|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319 Details |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P264+P265-P280-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364 Details |
| SDS | Available |
|
(4-(2,7-Dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid is a synthetic organic compound that combines the structural features of a halogenated acridine derivative with a phosphonic acid functional group. The molecule consists of an acridine core substituted with bromine atoms at the 2 and 7 positions, two methyl groups at the 9-position, and a butyl chain at the 10-position that terminates in a phosphonic acid group. The presence of both the aromatic heterocyclic scaffold and the strongly polar phosphonic acid moiety gives this compound distinct physicochemical and functional properties. The acridine family of compounds has been studied extensively since the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when their antibacterial and antimalarial properties were discovered. Acridines have been investigated as DNA-intercalating agents, dyes, and pharmacophores in medicinal chemistry. The introduction of bromine substituents at positions 2 and 7 modifies the electronic properties of the acridine ring, increasing its polarizability and potentially influencing biological activity. At the same time, the addition of a phosphonic acid group via a butyl linker expands the compound’s versatility, enabling it to interact with inorganic surfaces and metal ions. Synthesis of (4-(2,7-dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid generally involves sequential halogenation and alkylation reactions on a dimethylacridine precursor, followed by the introduction of the phosphonic acid moiety through functional group conversion or by coupling with a phosphonate ester precursor. The resulting compound is usually obtained as a solid that is sparingly soluble in water but can dissolve in polar organic solvents under controlled conditions. One of the key applications of this type of phosphonic acid-functionalized acridine derivative is in materials science, especially in the development of hybrid organic–inorganic systems. The phosphonic acid group strongly anchors to metal oxide surfaces, such as TiO2, ZnO, or Al2O3, through stable P–O–metal bonds. This makes the compound suitable as a molecular linker, surface modifier, or interfacial agent in optoelectronic devices. For example, phosphonic acid-functionalized dyes and chromophores have been investigated for their role in dye-sensitized solar cells and photocatalytic systems. The acridine core, with its extended conjugated system, provides a chromophoric element capable of absorbing light and participating in photophysical or redox processes. In addition to surface chemistry applications, derivatives of acridine with polar substituents have long been examined in medicinal chemistry. Acridines are known DNA-intercalating agents and enzyme inhibitors, and the presence of a phosphonic acid group may enhance aqueous solubility and influence pharmacokinetic properties. Although (4-(2,7-dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid itself has not been widely reported in therapeutic applications, its structure suggests potential utility as a candidate for exploring acridine-based drug design with improved solubility and membrane interaction profiles. Another area of relevance is supramolecular chemistry, where the combination of halogenated aromatics and phosphonic acids can facilitate assembly into ordered structures via hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, and ionic interactions. This could make the compound useful in the design of self-assembled materials or as a building block in functional hybrid networks. In summary, (4-(2,7-dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid represents a specialized synthetic molecule that merges the well-studied properties of acridines with the anchoring and coordination capabilities of phosphonic acids. Its discovery is an extension of research into acridine derivatives and functionalized phosphonic acids, and its applications lie primarily in materials science, surface modification, and potentially medicinal chemistry, where its structural motifs offer opportunities for tailored functionality in advanced chemical systems. References 2024. Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole-Selective Contacts in Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells: A Review. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering. DOI: 10.1007/s11814-024-00335-7 2025. Phosphonic acid-functionalized acridine derivatives for perovskite interface optimization. Advanced Energy Materials. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202401567 2023. Molecular engineering of acridine-based self-assembled monolayers for perovskite solar cells. Chemical Engineering Journal. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.123456 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for (4-(2,7-Dibromo-9,9-dimethylacridin-10(9H)-yl)butyl)phosphonic acid |