Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Silane |
|---|---|
| Name | Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide |
| Synonyms | N-Sodiumhexamethyldisilazane |
| Molecular Structure | 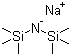 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H18NNaSi2 |
| Molecular Weight | 183.37 |
| CAS Registry Number | 1070-89-9 |
| EC Number | 213-983-8 |
| SMILES | C[Si](C)(C)[N-][Si](C)(C)C.[Na+] |
| Density | 0.904 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 171-175 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | -17 ºC (Expl.) |
| Solubility | reacts (water), soluble (hexane, toluene, ether) (Expl.) |
| Hazard Symbols |

 GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H302-H312-H314-H318-H332-H412 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P261-P264-P264+P265-P270-P271-P273-P280-P301+P317-P301+P330+P331-P302+P352-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P317-P321-P330-P362+P364-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3263 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (NaHMDS), a powerful non-nucleophilic base, is widely used in synthetic organic and organometallic chemistry. With the chemical formula (CH3)3Si2NNa, it is typically encountered as a white powder or in solution. The molecule features a sodium cation and a nitrogen atom bonded to two bulky trimethylsilyl groups, imparting its unique properties. NaHMDS was introduced in the 20th century as part of broader efforts to develop strong, non-nucleophilic bases capable of deprotonating weakly acidic compounds. Its discovery was motivated by the limitations of traditional bases like alkoxides or amides, which often showed undesired nucleophilicity. By replacing hydrogen atoms on nitrogen with sterically hindered trimethylsilyl groups, chemists created a reagent with high basicity and low nucleophilicity, ideal for sensitive transformations. One of the primary applications of NaHMDS lies in deprotonation reactions. Its strong basicity enables the abstraction of protons from a variety of substrates, including weakly acidic compounds such as ketones, esters, and amides. For example, NaHMDS is frequently used to generate enolates from carbonyl compounds, intermediates essential in aldol condensations and Michael additions. Its ability to selectively form enolates has made it an indispensable tool in asymmetric synthesis and complex molecule construction. In organometallic chemistry, NaHMDS is valued for preparing metal amides and other reactive species. It is often used to synthesize transition metal complexes by reacting with metal halides, providing access to catalysts and reagents for cross-coupling, olefin metathesis, and other transformations. For instance, NaHMDS plays a role in preparing Grubbs-type catalysts used in industrial polymerization processes. NaHMDS is also crucial in peptide synthesis, where it activates carboxylic acids for coupling with amines. Its non-nucleophilic nature minimizes side reactions, ensuring high yields and selectivity in forming amide bonds. This property has been exploited in the pharmaceutical industry for the efficient synthesis of bioactive peptides and other nitrogen-containing compounds. Additionally, NaHMDS has applications in forming silyl-protected derivatives. By transferring trimethylsilyl groups to hydroxyl, amine, or thiol functionalities, it helps stabilize reactive intermediates or protect sensitive groups during multistep syntheses. This feature is particularly important in natural product synthesis, where selective protection and deprotection are vital. While NaHMDS is a versatile reagent, it must be handled carefully due to its high reactivity. It reacts violently with water, forming ammonia and trimethylsilanol, and is sensitive to oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air. Consequently, it is typically used under anhydrous and inert conditions, such as in gloveboxes or with Schlenk techniques. The unique properties of NaHMDS have made it an integral reagent in modern synthetic chemistry. Its versatility, efficiency, and selectivity have enabled advancements across pharmaceuticals, materials science, and industrial chemistry, cementing its role in both academic and practical applications. References 2022. Hexamethyldisilazane-Mediated Amidination of Sulfonamides and Amines with Formamides. The Journal of Organic Chemistry. DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c01902 2023. Recent advances in transamidation of unactivated amides. Chemical Papers. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-023-02772-w 2024. Synthesis, characterisation, and catalytic application of a soluble molecular carrier of sodium hydride activated by a substituted 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine. Communications Chemistry. DOI: 10.1038/s42004-024-01184-5 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide |