Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| F&F Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (10) 6444-6910 | |||
 |
heyifnfchem@163.com heyi@fnfchem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1997 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2006 | ||||
| Kingfirst Chemical (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (25) 8452-2992 8477-3604 | |||
 |
marketing@kingfirstchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Dongtai Xinyuan Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (515) 8548-3100 (21) 5289-2866 | |||
 |
sales@xin-yuanchem.com xuxiaogang@9.cn | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2007 | ||||
| Simagchem Corporation | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13806087780 | |||
 |
sale@simagchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2002 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Changzhou Tianhua Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (519) 8289-1186 | |||
 |
tianhua@tianhuachem.com ctianhua@hotmail.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 1995 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2008 | ||||
| Qingdao Lilai Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (532) 8676-7976 | |||
 |
sales@lilaichem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (551) 6541-8684 | |||
 |
sales@tnjchem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2001 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Fatty acid |
|---|---|
| Name | Pimelic acid |
| Synonyms | 1,5-Pentanedicarboxylic acid; 6-Carboxyhexanoate; Heptanedioic acid |
| Molecular Structure | 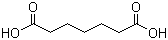 |
| Molecular Formula | C7H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 160.17 |
| CAS Registry Number | 111-16-0 |
| EC Number | 203-840-8 |
| SMILES | C(CCC(=O)O)CCC(=O)O |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.329 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 103 - 107 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 353.7±25.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 404.4 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | 181.9±19.7 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Solubility | ethanol: 0.1 g/mL, water: 25 g/L (13 ºC) (Expl.) |
| Index of refraction | 1.476 (Calc.)* point|103-106 ºC |
| Boiling point | 212 ºC (10 mmHg) |
| Water solubility | 25 g/L (13 ºC) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS07 Warning Details
GHS07 Warning Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P264-P264+P265-P271-P280-P302+P352-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P319-P321-P332+P317-P337+P317-P362+P364-P403+P233-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pimelic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid with the molecular formula C7H12O4. It consists of a seven-carbon linear chain terminated by carboxylic acid groups at both ends, classifying it as a straight-chain aliphatic dicarboxylic acid. Chemically, it is also known as heptanedioic acid and serves as a homolog in the series of α,ω-dicarboxylic acids between adipic acid (C6) and suberic acid (C8). The compound was first identified in the 19th century as a degradation product of naturally occurring fatty acids. Its name derives from the Greek word "pimele," meaning fat, reflecting its discovery in fatty material oxidation processes. Historically, pimelic acid has been obtained through the oxidative cleavage of unsaturated or polyunsaturated fatty acids, including oleic and linoleic acids, under conditions that break double bonds and leave terminal carboxyl groups. In modern synthetic chemistry, pimelic acid is produced by controlled oxidation of cycloheptanone or heptanedioic precursors using oxidants such as nitric acid or potassium permanganate. Alternative routes involve hydrolysis of pimelates, such as pimelic acid esters or amides, synthesized from ω-haloalkanoic acids or through carbon chain extension of shorter dicarboxylic acids using malonic acid derivatives. These methods provide high-purity material for laboratory and industrial use. Pimelic acid has significant value as a building block in the synthesis of polymers, resins, and plasticizers. Its two carboxylic acid groups allow it to form condensation polymers when reacted with diols or diamines, leading to the formation of polyesters or polyamides. It has been used in the synthesis of nylon-type polyamides, although less frequently than shorter-chain analogs like adipic acid. The chain length of pimelic acid imparts intermediate flexibility and crystallinity to the polymer products, making it suitable for specialty material applications. In biochemistry, pimelic acid holds particular importance as a biosynthetic precursor in the formation of biotin (vitamin B7). In many microorganisms and plants, pimeloyl-CoA, a coenzyme A-activated form of pimelic acid, serves as a key intermediate in the early steps of biotin biosynthesis. This involvement in cofactor biosynthesis has been well studied in species such as *Escherichia coli*, where the origin and regulation of pimelic acid pathways are essential for growth and development. The ability of organisms to synthesize pimelic acid from malonyl-ACP and other fatty acid derivatives has also been investigated in metabolic engineering studies. Beyond its biological role, pimelic acid is used in coordination chemistry and supramolecular chemistry due to its two terminal carboxyl groups and the flexible aliphatic chain between them. These features enable it to act as a bidentate ligand or as a spacer in metal–organic frameworks and other host–guest systems. The seven-carbon length offers an ideal separation for tuning the spatial arrangement of metal centers or functional groups in extended structures. Pimelic acid has also been employed in the preparation of esters used as synthetic lubricants, cosmetic additives, and plasticizers. Its esters with simple alcohols provide good thermal and oxidative stability, making them suitable for demanding formulation environments. Additionally, its water solubility is low, but its solubility in alcohols and polar organic solvents is moderate, which aids in its use in solvent-based reaction systems. The compound is typically handled as a white crystalline solid with a melting point around 105 °C. It is stable under standard conditions and does not pose significant safety concerns beyond general precautions for handling organic acids. It is classified as a low-toxicity material and is biodegradable, adding to its appeal in sustainable chemical applications. Pimelic acid remains a representative example of medium-chain aliphatic diacids with utility spanning synthetic organic chemistry, industrial polymer production, and biological metabolism. Its intermediate chain length and bifunctional reactivity provide versatility for applications requiring both chemical performance and biological compatibility. References 1883. Zur Kenntniss der Pimelinsäure. Monatshefte für Chemie und verwandte Teile anderer Wissenschaften. DOI: 10.1007/bf01517976 1934. über die Darstellung der Pimelinsäure. Monatshefte für Chemie und verwandte Teile anderer Wissenschaften. DOI: 10.1007/bf01522045 |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Pimelic acid |